Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs)
A printed circuit board (PCB) is a rigid or flexible laminated board with patterned copper conductors that route electrical signals, distribute power, and mechanically support electronic components.
Anatomy of Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs)
PCBs are composed of distinct layers, with single-layer PCBs using a simpler structure and multi-layer PCBs adding internal layers and vias. Printed circuit boards (PCBs) are composed of distinct material layers that provide mechanical support, electrical connectivity, and component identification. While single-layer PCBs use a simplified structure, multi-layer PCBs incorporate additional internal layers and vias to support higher circuit density and performance requirements.
Single-Layer Printed Circuit Boards
Simplified PCB Architecture
Single-layer PCBs consist of one conductive copper layer bonded to an insulating substrate. All electrical connections and component pads are formed on the same side of the board, making this PCB type cost-effective and suitable for low-complexity electronic designs.
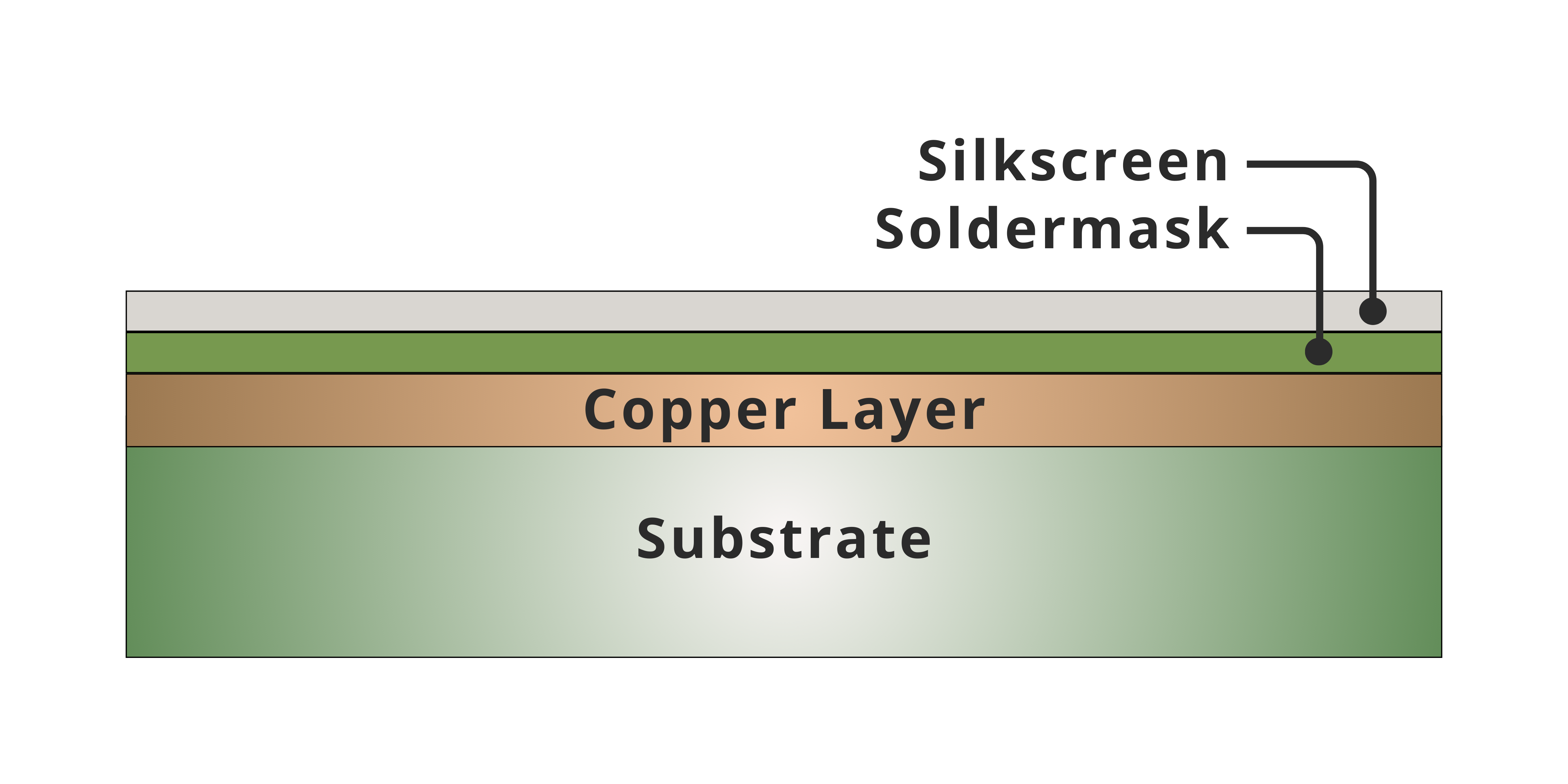
Substrate Layer
Insulating base material of the PCB, typically FR-4, CEM-1, or polyimide for flexible PCBs, providing mechanical strength and electrical isolation.
Conductive Copper Layer
Patterned copper foil forming traces and pads, creating electrical connections between components on the PCB.
Solder Mask
Protective polymer coating applied over the copper layer, leaving pads exposed to prevent solder bridging and oxidation.
Silkscreen
Printed markings that indicate component placement, polarity, and reference designators to support assembly and maintenance.
Multi-Layer Printed Circuit Boards
High-Density PCB Architecture
Multi-layer PCBs consist of two or more conductive copper layers separated by insulating dielectric materials. This architecture enables significantly higher routing density in a compact footprint while improving signal integrity, power distribution, electromagnetic interference (EMI) control, and compatibility with modern high-pin-count components.
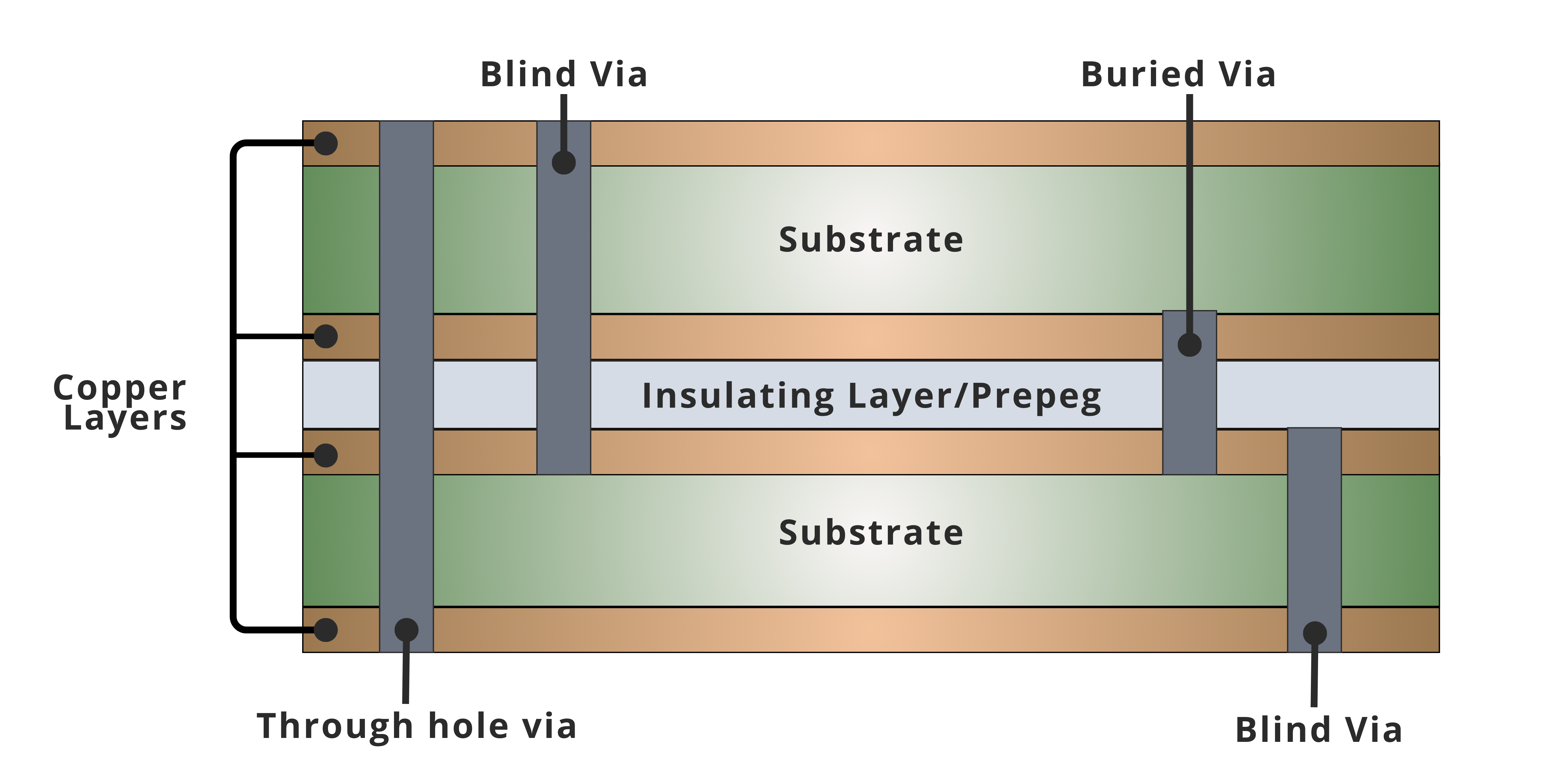
Inner Copper Layers
Additional patterned copper layers embedded within the PCB to support signal routing, power planes, and ground planes beyond the outer surfaces.
Dielectric Layers
Insulating core and prepreg materials placed between copper layers to provide electrical isolation and bond the PCB stack into a laminated structure.
Vias
Plated holes that create electrical connections between copper layers, enabling vertical signal routing throughout the PCB stack.
PCB Market by Application (2020–2025)
Baseline PCB market value.
Post-pandemic recovery and demand rebound.
Mid-single-digit CAGR outlook.
Projected sustained growth rate.
Printed circuit boards (PCBs) form the electrical and mechanical foundation of modern electronics. Through copper traces, pads, and layered insulation, PCBs provide controlled signal routing, power distribution, and structural support for mounted components. These functions enable reliable integration of processors, memory, sensors, and power electronics into compact, high-performance systems.
Because of their central role, PCBs are used across a broad range of applications including consumer electronics, industrial equipment, automotive systems, and communication infrastructure. Market growth is therefore closely tied to trends in device complexity, electrification, connectivity, and automation rather than unit volume alone.
PCB Demand Concentrated Across Four Core End Markets
Consumer Electronics (~30%) represents the largest share of global PCB demand, driven by smartphones, wearables, TVs, and IoT devices. High-layer count and HDI boards continue to dominate this segment as device density and functionality increase.
Industrial Electronics (~10–15%) includes automation, controls, medical devices, and appliances. After contracting in 2020, industrial PCB demand has recovered alongside factory modernization and post-pandemic medical investment.
Automotive Electronics (~14–15%) is one of the fastest-growing segments, reaching approximately $10.6B in 2024. Growth is fueled by EV power electronics, ADAS, infotainment, and vehicle connectivity.
Communication & Telecom (~15–20%) includes networking equipment, base stations, and wireless infrastructure. Expansion of 5G networks and data center connectivity continues to support demand in this segment.
While PCBs provide the structural and electrical backbone of electronic systems, long-term performance depends heavily on PCB assembly materials. Adhesives, conformal coatings, thermal interface materials, and interconnect products determine how components are mounted, protected, cooled, and electrically connected throughout the service life of the assembly.
As PCB complexity and operating demands increase across consumer, industrial, automotive, and communication applications, material selection becomes a critical factor in ensuring durability, reliability, and compliance with evolving performance requirements.
Sources: Prismark Partners, Mordor Intelligence, Fortune Business Insights, TTM Technologies filings
PCB Assembly
These process steps define how modern PCB assemblies achieve consistent electrical performance, mechanical stability, and long-term reliability across industries.
Automated stencil printing, pick-and-place, and reflow soldering deliver consistent placement accuracy, high throughput, and process repeatability in volume PCB manufacturing.
Modern PCB assemblies combine surface-mount, through-hole, and selective hand-soldered processes to meet electrical, mechanical, and thermal performance requirements.
Cleaning, inspection (SPI/AOI), protective coatings, thermal materials, and final electrical testing are critical to ensuring durability and functional reliability.
Solutions for Printed Circuit Board Assemblies
PCB assembly relies on a range of specialized materials beyond the printed circuit board itself. While the PCB provides the electrical and mechanical foundation, additional materials are required to form reliable interconnections, remove process residues, protect assemblies from environmental exposure, and manage heat during operation.
- Solders, solder pastes, fluxes
- conductive adhesives
- die-attach materials
- surface-mount adhesives
- solder preforms
Reliable materials used to create durable electrical and mechanical connections.
- Flux cleaners
- Defluxing agents
- Precision cleaning solvents
Designed to remove residues from soldering and handling processes.
- Conformal coatings
- potting and encapsulation compounds
- Waterproofing materials
- Board-level underfills
Protection that shields assemblies from moisture, chemicals, vibration, and mechanical stress.
used to control temperature and improve system reliability.
Humiseal Conformal Coatings for Printed Circuit Boards
Conformal Coatings best suited for your application
An easy way to protect a PCB and increase its longevity is to apply a Conformal Coating. A conformal coating is a thin film specifically designed to safeguard electronic assemblies. It can protect from dust, corrosion, and moisture by creating a protective layer that envelopes the PCB and all its components. Conformal coatings also electrically insulate the PCB, reducing the risk of electrical failures.
.png)

HumiSeal™ Conformal Coatings are based on different chemistries, including acrylics, silicones, synthetic rubbers, and UV-curable acrylates. Each chemistry offers distinct properties suited for specific application requirements, such as electrical insulation, moisture resistance, chemical protection, or mechanical flexibility. These coatings are also available with varied curing mechanisms (e.g. moisture, heat, UV), allowing compatibility with different production speeds and process constraints.
Featured Products
Excellent chemical resistance
Durable, tough coating
Ideal for harsh environments
Easy apply & rework
Strong moisture resistance
Clear, cost-effective protection
Extreme temperature stability
Flexible & stress-relieving
Excellent moisture protection
Flexible, vibration-resistant
Moisture & salt protection
Easy to repair/remove
Fast UV curing
Clear, moisture-resistant
Ideal for automation
Hard, durable finish
Superior chemical barrier
Strong substrate adhesion
Key Features and Benefits of HumiSealTM Conformal Coatings
- Moisture protection, which prevents corrosion and electrical shorting in electronic assemblies
- Chemical resistance, which safeguards components from harsh environmental contaminants
- Dielectric insulation, which maintains circuit integrity and prevents arcing between conductors
Frequently Asked Questions About Conformal Coatings
▶ How does a conformal coating work?
The liquid coating conforms to every contour of the electronic assembly, forming a continuous protective film. This layer shields components from moisture, dust, chemicals, and electrical leakage while maintaining electrical isolation and long-term reliability.
▶How do I choose the right conformal coating chemistry?
Selecting the appropriate conformal coating depends on environmental exposure, operating temperature range, humidity, mechanical stress, chemical resistance requirements, and reworkability needs.
Common coating chemistries include:
- Acrylics – easy to apply and rework, limited high-temperature resistance
- Silicones – excellent for high humidity, wide temperature ranges, and vibration
- Polyurethanes – strong resistance to solvents and abrasion
- UV-curable – ideal for high-speed, inline manufacturing processes
▶How is a conformal coating applied?
Conformal coatings can be applied using several methods, depending on production volume, coating type, and coverage requirements.
- Hand brushing
- Hand dispensing
- Spray coating (aerosol or hand spray)
- Dip coating
- Automated selective coating
▶Can conformal coatings be applied selectively?
Yes. Automated selective coating systems precisely deposit coating only where protection is required, leaving connectors, sockets, and test points exposed. This minimizes masking, reduces material usage, and improves process consistency.
▶What surface preparation is required before coating?
Surface cleanliness is critical for coating adhesion and reliability. Assemblies must be free of flux residues, oils, and particulates. Common preparation methods include aqueous washing, plasma cleaning, and ionized air cleaning.
IPC-CC-830 recommends ionic contamination levels below 1.56 µg/cm² NaCl equivalent prior to coating.
▶How do conformal coatings perform under thermal cycling and mechanical stress?
Performance varies depending on coating chemistry and operating conditions:
- Silicones – perform best under wide thermal ranges (–55 °C to +200 °C) and vibration
- Acrylics and epoxies – may crack or delaminate under extreme flexing or rapid thermal cycling
Protection Solutions with Aculon's PCB Waterproofing Treatments
Nanoscale surface treatment designed to impart hydrophobicity
Certain applications may require waterproofing, such as underwater equipment or electronics like smartphones and watches. In these cases, nanocoatings are a great way to achieve various levels of waterproofing. Aculon's PCB Waterproofing Treatments provide an extremely thin coating that adds hydrophobicity without altering the surface of the PCB. The goal of these treatments is to protect the PCB from short circuits and other damage caused by moisture, which can cause corrosion and degrade the performance of the circuit over time.
Aculon's NanoProof™ Series offers customers a range of PCB waterproofing solutions from protecting against accidental water damage to IPX7, immersion in water at one-meter depth for 30 minutes, to greater barrier properties that can withstand 100 hours of immersion in sweat solutions and some of the most stringent test methods developed for non-hermetic components. Some Waterproofing Treatments Caplinq offers include:
- Nanoproof 1.0 - IPX4, best for a broad range of substrates
- NanoProof 2.1 - best for PCBs and electronic components
Treatments depend on various factors including substrate, hydrophobicity or oleophobicity level, coating thickness, etc.
Industrial Control & Consumer Electronics
Industrial and consumer electronics increasingly operate in environments exposed to humidity, salt spray, noxious gases, and continuous operation. Conformal coatings help prevent performance degradation and unplanned downtime.
Typical applications include motor drives, power supplies, HVAC controls, backup power systems, and critical sensors.
Automotive Electronics
Automotive electronics demand resistance to vibration, temperature extremes, and chemical exposure. Rubber-based conformal coatings are commonly used due to their flexibility and wide operating temperature range from –65 °C to +150 °C.
Applications include safety systems, radar sensors, ECUs, lighting systems, cameras, and power control modules throughout the vehicle.
Conformal coatings are highly effective environmental filters but are not fully impermeable. For applications requiring full waterproofing, specialized PCB waterproofing treatments or potting solutions are recommended.
Support reliable PCB Assembly Materials and Protection.
We have everything you need to make your PCB assembly the best that it can be. Contact us to discuss conformal coating selection, material compatibility, and long-term reliability considerations for different PCB assemblies.
Featured Presentation: CAPLINQ Product Offerings
CAPLINQ Conformal Coatings for Printed Circuit Boards
Curious about how the right materials can improve PCB Performance? This quick presentation walks you through CAPLINQ’s lineup for Conformal Coatings: what they’re made of, how they perform, and where they fit best. Whether you’re optimizing for efficiency, durability, or both, these materials are engineered to keep up.
Got questions or need help choosing the right materials for your Printed Circuit Boards? Reach out to us!
Contact Us →Presentations
Related Blogs

Mitigating Tin Whiskers in Military and Aerospace Electronics with Conformal Coatings?
This blog discusses tin whiskers in military and aerospace electronics and how they can cause failures. It explains how conformal coatings help mitigate these risks by containing whisker growth and preventing electrical shorts, while highlighting the effectiveness of different coating types.

How to Select the Right Conformal Coating
This blog guides readers through the process of choosing the right conformal coating for electronics. It explains the main coating types (acrylic, urethane, silicone, rubber‑based, UV‑curable), compares their strengths (e.g., temperature resistance, moisture resistance, flexibility), and shows how to match the chemistry to your application needs.



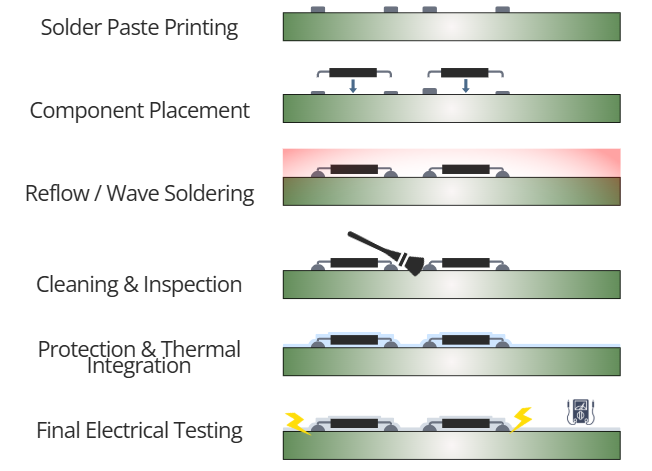 Automated PCB assembly line illustrating stencil printing, component placement, and soldering
Automated PCB assembly line illustrating stencil printing, component placement, and soldering