Semiconductors
- An energy source, like a battery
- An open circuit
- And a reference on this circuit - let's say an LED lamp.
Copper, Iron, Silver, Aluminium for example are known conductors so if we use them to close the gap our lightbulb will turn on.
If we use a non conductive material though, such as Paper, glass, rubber, porcelain or ceramic, the light will stay off.
Basics of Electrical conductivity
To understand why this happens we have to go back to high school physics.
- Single atoms have energy levels.
- Multiple interacting atoms slightly adjust their energy levels to each other
- Billions of atoms together, as in the case of solids, create energy bands. These energy bands can be non existent, medium or wide.
If the gap within the band is small then the electrons can easily jump to a higher energy state and conduct electricity.
If the gap is wide, the electrons cannot reach the higher state and so the material is insulating since the current can't flow.
Theoretically, if we apply enough energy/heat/light/electric fields we can make these insulators conduct but this is not feasible because either the amounts of energy required would be too high or the materials would break before they could reach this small band gap state.
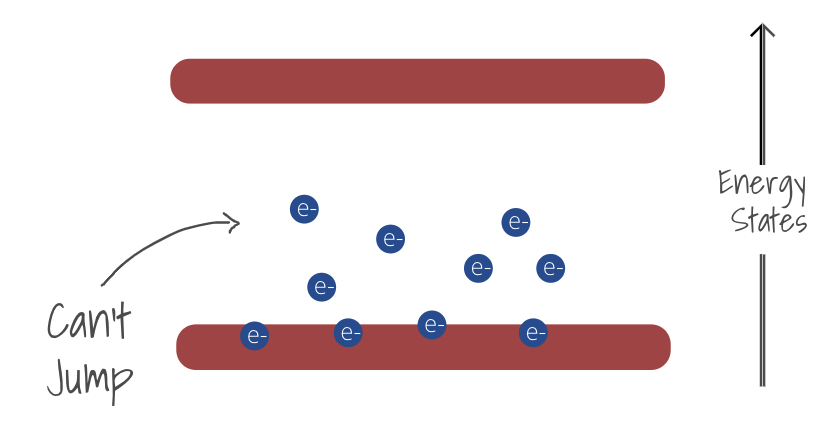
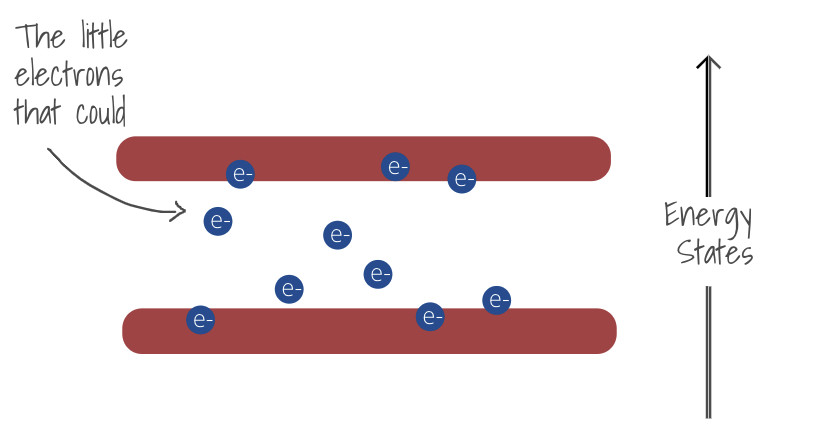
How Semiconductors work
Their band gap is wide enough so that they don't conduct electricity (making them insulators by nature). But if we apply some energy then the gap shrinks enough for the electrons to jump to a higher state and for the materials to conduct, making them semi-conductors. Current flow can also be adjusted by regulating the energy flows.
In the electronics industry the most popular semiconductor material is Silicon (Si) but there are also a multitude of other materials such as Gallium arsenide(GaAs), Silicon carbide(SiC), Gallium Nitride(GaN) used for higher voltage and high power applications.
It's really hard to overstate the importance of semiconductors in our lives. No semiconductors would mean no transistors, no computers and no information age. Our phones, laptops, tvs, cars, hell refridgerators all contain some sort of semiconductor in them.
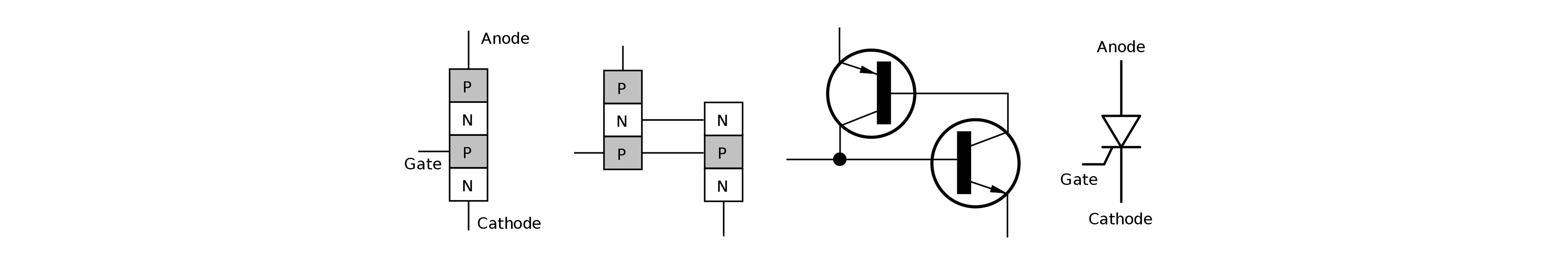
Semiconductors are used to create the brains of every single modern electronics packaging. There are multiple types of semiconductor packages with multiple layers of complexity, from simple transistors to advanced packaging configurations, and we offer materials for every single step of the way.
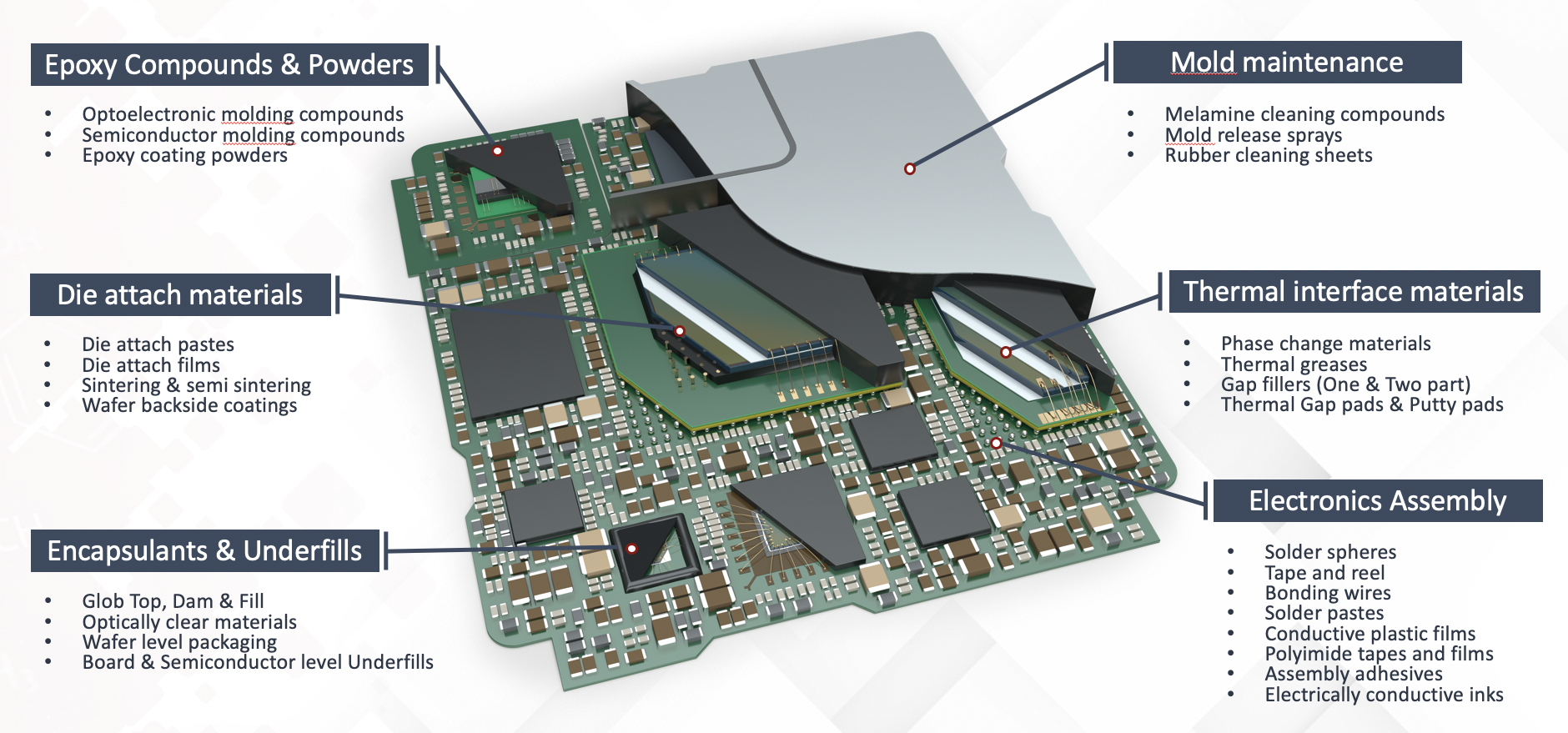
Please check all our semiconductor pages below where we focus on specific type and package requirements and suggest suitable products for each application.
We are trying to go in depth into the key application considerations and suggest products based on the most important properties. But since there is an infinite amount of packages and configurations please contact us for a custom made solution to your design and processing requirements.
Optoelectronics in Semiconductors
Optoelectronics is a vital branch of semiconductor technology that bridges the gap between optics and electronics, enabling the conversion of electrical signals into light and vice versa. From LEDs and laser diodes to photodetectors and image sensors, optoelectronic components are foundational to a wide range of modern applications, including optical communication, sensing, display technologies, and advanced imaging systems. These devices rely heavily on semiconductor materials such as gallium arsenide (GaAs), indium phosphide (InP), and silicon photonics, to achieve high-performance light emission, detection, and modulation. As demand grows for faster data transmission, smarter sensors, and energy-efficient lighting, optoelectronics continues to play a crucial role in shaping the future of high-tech industries.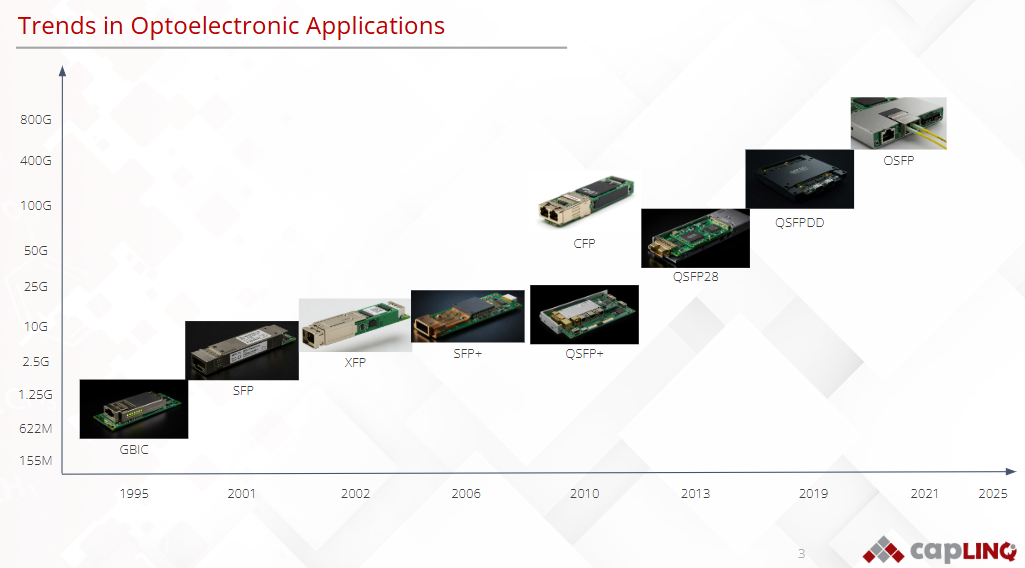
Next generation applications will utilize larger and higher power ASICs/FPGAs for data processing/transfer.