PTM6880 | Phase Change Pad
- 6,0 W/m•K thermal conductivity
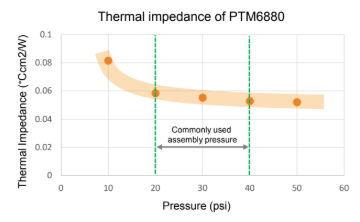
- 0.056 ℃•cm²/W
- Improved flowability
Product Description
PTM6880 is a high-performance phase change material engineered for next-generation high-power semiconductor packaging. With a bulk thermal conductivity of 6.0 W/m·K and thermal impedance as low as 0.056 °C·cm²/W, it delivers highly efficient thermal management in dense electronic assemblies. Its robust non-pump-out formulation ensures stable performance even under aggressive thermal cycling and mechanical stress.
Built on a novel PCM polymer system with optimized filler loading, PTM6880 maintains reliability through 1000 thermal shock cycles and extended high-temperature aging. The material activates at a 45 °C phase change temperature, allowing it to conform to surface irregularities, reduce interfacial resistance, and achieve extremely thin bond lines—making it ideal for advanced, high-power applications.
Key Features
- 6.0 W/m·K thermal conductivity
- Ultra-low thermal impedance: 0.056 °C·cm²/W
- Outstanding non-pump-out performance under thermal cycling
- 45 °C phase change temperature for rapid interface wetting
- Optimized for bond line thickness < 1.5 mil (0.038 mm)
- Available in pad format (paste version coming soon)
Target Applications
- AI and machine learning accelerators (GPU/ASIC)
- High-power CPUs and SoCs in enterprise servers
- Power modules and converters for automotive & industrial systems
- High-density telecom and 5G base station electronics
- Networking switches, routers & optical transport hardware
- High-bandwidth memory (HBM) and advanced 2.5D/3D packaging
- High-reliability embedded and industrial control electronics
Technical Specifications
| General Properties | |
| Specific Gravity Specific Gravity Specific gravity (SG) is the ratio of the density of a substance to the density of a reference substance; equivalently, it is the ratio of the mass of a substance to the mass of a reference substance for the same given volume. For liquids, the reference substance is almost always water (1), while for gases, it is air (1.18) at room temperature. Specific gravity is unitless. | 2.7 |
| Thermal Properties | |
| Thermal Conductivity Thermal Conductivity Thermal conductivity describes the ability of a material to conduct heat. It is required by power packages in order to dissipate heat and maintain stable electrical performance. Thermal conductivity units are [W/(m K)] in the SI system and [Btu/(hr ft °F)] in the Imperial system. | 6 W/m.K |
| Thermal Impedance | 0.056 °C·cm²/W |
| Electrical Properties | |
| Volume Resistivity Volume Resistivity Volume resistivity, also called volume resistance, bulk resistance or bulk resistivity is a thickness dependent measurement of the resistivity of a material perpendicular to the plane of the surface. | 2.0x1014 Ohms⋅cm |
Additional Information
Frequently Asked Questions About PTM6880 (High thermal conductivity phase change pad, 6.0 W/m·K, 45 °C PCM)
What are typical applications for PTM6880?
PTM6880 is designed as a high-performance phase change thermal interface material for high-power, high-density electronics where very low thermal resistance and long-term reliability are critical.
- AI accelerators, GPUs and CPUs in hyperscale and enterprise data centers
- Power modules, converters and inverters in automotive and industrial drives
- Telecom base stations, 5G radios, networking and optical transport equipment
Why choose PTM6880 over alternatives?
PTM6880 combines a bulk thermal conductivity of 6.0 W/m·K with a thermal impedance as low as 0.056 °C·cm²/W at 80 °C and 35 psi, achieving excellent performance at bond line thicknesses below 1.5 mil (0.038 mm). Its novel PCM polymer system delivers strong interface wettability, very low contact resistance, and a super non-pump-out behavior verified through 1000 hours of high-temperature ageing, 85 °C/85 %RH exposure, and 1000 thermal shock cycles.
What is the shelf life of PTM6880?
When stored in the original, unopened packaging under recommended warehouse conditions (typically 19–24 °C and relative humidity <65 %), PTM phase change pads have a typical shelf life of 12 months from date of manufacture at 23 ±2 °C. Always refer to the product label and latest technical documentation for the specific lot shelf life and storage guidance.
How do I clean tools after applying PTM6880?
Since PTM6880 is supplied in pad format, tool contamination is usually minimal. If fixtures, clamps or handling tools come into contact with the material, residue can typically be removed mechanically (wiping or gentle scraping) at or slightly above the phase change temperature, followed by cleaning with an appropriate solvent-compatible wipe approved for your production line. Avoid aggressive abrasives that could damage the mounting surfaces.
What happens after shelf life?
Beyond the recommended shelf life, PTM materials may begin to absorb moisture or experience subtle changes in rheology that can affect handling and long-term reliability, even if initial thermal impedance still appears within specification. Internal studies on similar Solstice PCM products have shown that thermal performance can remain stable in some cases, but use of expired material is at the customer’s own risk and should only be considered after a formal requalification (thermal impedance, BLT and visual inspection) according to the application’s criticality.
How do I cure PTM6880?
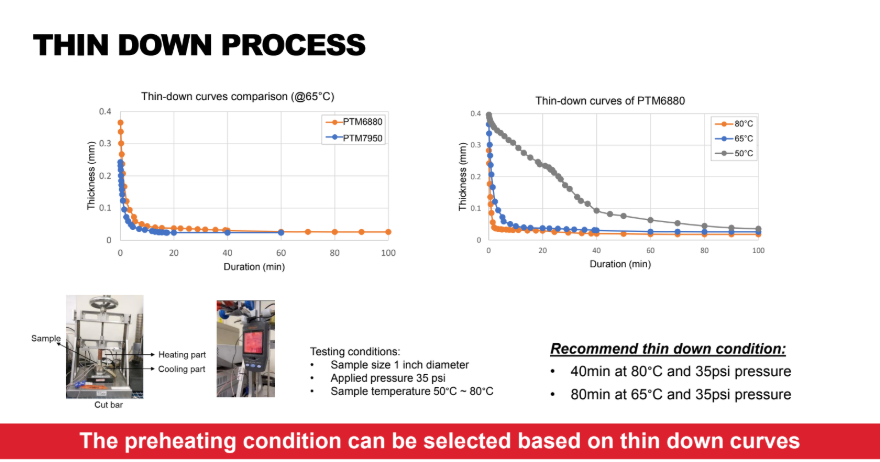
PTM6880 is a phase change material and does not require a chemical cure. Instead, it must be heated above its phase change temperature of approximately 45 °C under clamp pressure so that it softens, wets the mating surfaces and thins down to the target bond line thickness. Typical assembly processes compress the pad at 35 psi and heat the interface to 65–80 °C for 40–80 minutes, allowing the material to reach a stable, low-impedance state before normal device operation.
What thickness should I apply?
For best performance, PTM6880 is designed to operate at a bond line thickness below 1.5 mil (0.038 mm). Under typical conditions (35 psi, 60–80 °C), the pad will thin down to around 20 µm in the test configuration, balancing low thermal resistance with good mechanical compliance. The optimal starting pad thickness and clamp pressure depend on the module design, warpage and gap; Solstice's thin-down curves and gap-change cycling data can be used to select the right stack-up for your application.
How is it applied and removed?
PTM6880 is supplied as die-cut pads on a carrier liner or in reel format. Application typically involves aligning the pad to the device or heat spreader, peeling the liner, placing the assembly, and applying clamp pressure and temperature to drive the phase change and thin-down. For rework, the interface is reheated above the phase change temperature and the heat sink is gently separated; residual material can then be peeled or wiped away and replaced with a fresh pad.
What temperatures can it withstand?
PTM6880 is designed for electronic operating and reliability test conditions ranging from sub-zero to high-temperature stress. Reliability data shows stable thermal impedance after 1000 hours of baking at 150 °C, 1000 hours at 85 °C/85 %RH, and 1000 cycles of thermal shock between –40 °C and +125 °C, demonstrating suitability for demanding AI server, telecom and automotive-style environments.
Any safety or storage tips?
Store PTM6880 in its original, sealed packaging at 19–24 °C and <65 % relative humidity, away from direct heat sources. Avoid exposing reels or pads to temperatures above 40 °C during transport and storage to prevent premature softening between cuts. Allow cold shipments to equilibrate to room temperature before opening to minimize condensation on the pad surfaces. Always consult the Safety Data Sheet (SDS) and follow your facility’s PPE and handling guidelines.
Learn More About PTM6880 (High thermal conductivity phase change pad, 6.0 W/m·K, 45 °C PCM)
PTM6880 is a high-performance phase change thermal interface pad engineered for advanced semiconductor packaging. It delivers 6.0 W/m·K bulk thermal conductivity and achieves thermal impedance as low as 0.056 °C·cm²/W at typical assembly conditions, thanks to a novel PCM polymer system and highly loaded conductive fillers. With a phase change temperature around 45 °C and excellent thin-down behavior, PTM6880 rapidly wets the interface and forms a thin, uniform bond line that supports high heat flux in AI, data center, power and telecom applications.
Key Features at a Glance
- ✔ 6.0 W/m·K bulk thermal conductivity for high heat flux designs
- ✔ Thermal impedance as low as 0.056 °C·cm²/W at 80 °C, 35 psi
- ✔ Phase change temperature at ~45 °C for fast interface wetting
- ✔ Optimized for bond line thickness < 1.5 mil (0.038 mm)
- ✔ Proven reliability: 150 °C bake, 85/85 and –40 °C to +125 °C thermal shock testing
- ✔ Super non-pump-out behavior under gap change and cycling
| Properties | Value | Method |
| Thermal impedance (@80°C, 35psi) | 0.056 °C∙cm2/W | ASTM D5470 |
| Density | 2.7 g/cm3 | ASTM D792 |
| Phase change temperature | 45°C | DSC |
| Thermal conductivity | 6.0 W/m∙K | ASTM D5470 |
| Bond line thickness (@60°C, 20psi) | 20μm | HON internal |
Versatile Application Methods
Application Methods
PTM6880 is supplied as precision die-cut pads in sheet or reel format for automated or manual placement. The pad is aligned to the device or heat spreader, the release liner is removed, and the assembly is clamped under defined pressure. A controlled preheat step to 65–80 °C allows the material to phase-change, flow and thin down to the target bond line thickness, after which the hardware can be cooled and put into service.
Application Compatibility
- Suitable for lidded and lidless packages, heat spreaders and cold plates
- Works with copper, aluminum and nickel-plated interfaces
- Supports both vertical and horizontal module orientations without pump-out
High-Performance Thermal Management
PTM6880 delivers exceptionally low thermal resistance at thin bond lines, using its 6.0 W/m·K thermal conductivity to efficiently spread heat from high-power dies into heat sinks or cold plates. Once the material phase-changes at ~45 °C, it rapidly wets the interface, reducing contact resistance and enabling uniform heat transfer in high-density electronics such as AI accelerators, CPUs, GPUs, and power modules.
A key advantage of PTM6880 is its ability to achieve and maintain sub-1.5 mil (0.038 mm) bond line thicknesses. This thin-down behavior forms a stable, low-impedance thermal path that minimizes junction temperature rise during continuous high-load operation. The material is specifically engineered for environments where sustained heat flux and tight mechanical tolerances require consistent interface performance.
Extensive reliability testing, including 1000 hours at 150 °C, 1000 hours at 85 °C/85% RH, and 1000 thermal shock cycles between –40 °C and +125 °C, demonstrates that PTM6880 maintains its thermal impedance, adhesion, and structural integrity under extreme conditions. This ensures dependable long-term cooling performance for data center servers, telecom infrastructure, automotive power modules, and other mission-critical systems where thermal stability is essential.
Gap Stability & Pump-Out Control 💡
PTM6880 is specifically engineered to prevent pump-out in demanding, high-cycling environments. In solstice’s internal Pumping Out Risk Evaluation, PTM6880 demonstrated exceptionally stable thermal resistance compared to conventional phase change materials.
During the thickness cycling test—designed to simulate real-world warpage between heat sources and heat sinks (gap variation between 120 µm and 70 µm)—PTM6880 showed only a 30–42% increase in thermal resistance over 750 cycles. This low shift reflects strong adhesion, mechanical stability and minimal material displacement under thermal stress.
By contrast, higher pump-out PCMs such as PTM7950 demonstrated thermal resistance increases up to 119%, further highlighting PTM6880’s superior mechanical stability and resistance to material displacement. This ensures consistent long-term heat transfer efficiency, especially in applications subject to frequent thermal cycling or mechanical warpage such as power modules, advanced CPUs, and automotive electronics.
Compliance You Can Trust ✅
PTM6880 is engineered for use in modern electronic hardware and is supported by solstice’s global quality and environmental management systems. The product is supplied with detailed technical data, reliability reports and safety documentation to help OEMs and EMS partners meet their internal qualification, reliability and environmental requirements.
- Supports qualification to typical server, telecom and power electronics reliability standards
- Backed by Solstice’s documented reliability testing (thermal ageing, 85/85, thermal shock)
- Available technical data for system-level thermal modelling and design-in
- Global technical support for process and application optimization
- Traceable manufacturing and lot control for high-volume production
- Safety Data Sheet (SDS) and handling guidelines available upon request