ABchimie836UV Soft Dual Cure Conformal Coating
- One Component
- Dual Cure (UV and Humidity)
- Excellent Moisture Resistance
Product Description
ABChimie® 836UV is a transparent urethane acrylate conformal coating designed to provide mechanical and environmental protection to electronic components and assemblies. It features dual-cure technology (UV and humidity), which allows for the complete crosslinking through the entire PCB, even in areas that may be covered by shadow. The coating also allows the PCB to be soldered through without producing toxic gases.
ABChimie 836UV exhibits excellent moisture resistance in humid environments (Log Ohm> 10.5, IPC CC 830, SIR per IPC TM 650 2.6.3.4), which makes it ideal for conformal coating applications. The ideal application method is selective coating. One of its advantages is that it cures rapidly under UV light, has zero VOCs, and can be applied to high-speed manufacturing processes to increase productivity. ABChimmie 836UV is in full compliance with REACH and RoHS regulations, and also has UL94 V0 and UL746E (QMJU2-E308681) certifications.
Product Key Features
- Transparent
- Dual Cure (UV + Humidity)
- Thin film thickness (30 - 130 microns)
- Excellent adhesion to PCBs
- Resists mold growtn
- Fast UV cure for high volume production
- Solvent-free formulation (no VOCs)
- Spray and Selective Coating (ideal) applications
- UL94 V0 and UL746e
Applications - Conformal coating for Printed circuit assemblies.
- Protection for plastic casings or covers
Technical Specifications
| General Properties | |
| Appearance Appearance Appearance at room temperature. | Transparent liquid |
| Film Thickness Film Thickness Film thickness is the thickness of a backing film without taking into account any coatings or adhesive layers. It is measured in micron and the conversion factor to mil is 0.039. | 30 - 130 µm |
| Electrical Properties | |
| Breakdown Voltage Breakdown Voltage Breakdown voltage is the minimum voltage necessary to force an insulator to conduct some amount of electricity. It is the point at which a material ceases to be an insulator and becomes a resistor that conducts electricity at some proportion of the total current. After dielectric breakdown, the material may or may not behave as an insulator any more because of the molecular structure alteration. The current flow tend to create a localised puncture that totally alters the dielectric properties of the material. This electrical property is thickness dependent and is the maximum amount of voltage that a dielectric material can withstand before breaking down. The breakdown voltage is calculated by multiplying the dielectric strength of the material times the thickness of the film. | 1500 V |
| Thermal Properties | |
| Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (CTE), α1 Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (CTE), α1 CTE α1 (alpha 1) is the slope of the Coefficient of thermal expansion in a temperature range below the Glass transition temperature (Tg). It explains how much a material will expand until it reaches Tg. | 66 ppm/°C |
| Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (CTE), α2 Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (CTE), α2 CTE α2 (alpha 2) is the slope of the Coefficient of thermal expansion in a temperature range above the Glass transition temperature (Tg). It explains the extent to which a material will expand after it passes Tg. | 193 ppm/°C |
| Glass Transition Temperature (Tg) Glass Transition Temperature (Tg) The glass transition temperature for organic adhesives is a temperature region where the polymers change from glassy and brittle to soft and rubbery. Increasing the temperature further continues the softening process as the viscosity drops too. Temperatures between the glass transition temperature and below the decomposition point of the adhesive are the best region for bonding. The glass-transition temperature Tg of a material characterizes the range of temperatures over which this glass transition occurs. | 35 °C |
| Operating Temperature | -50 - +150 °C |
| UL 94 Rating UL 94 Rating Flammability rating classification. It determines how fast a material burns or extinguishes once it is ignited. HB: slow burning on a horizontal specimen; burning rate less than 76 mm/min for thickness less than 3 mm or burning stops before 100 mm V-2: burning stops within 30 seconds on a vertical specimen; drips of flaming particles are allowed. V-1: burning stops within 30 seconds on a vertical specimen; drips of particles allowed as long as they are not inflamed. V-0: burning stops within 10 seconds on a vertical specimen; drips of particles allowed as long as they are not inflamed. 5VB: burning stops within 60 seconds on a vertical specimen; no drips allowed; plaque specimens may develop a hole. 5VA: burning stops within 60 seconds on a vertical specimen; no drips allowed; plaque specimens may not develop a hole | V-0 |
| Physical Properties | |
| Viscosity Viscosity Viscosity is a measurement of a fluid’s resistance to flow. Viscosity is commonly measured in centiPoise (cP). One cP is defined as the viscosity of water and all other viscosities are derived from this base. MPa is another common unit with a 1:1 conversion to cP. A product like honey would have a much higher viscosity -around 10,000 cPs- compared to water. As a result, honey would flow much slower out of a tipped glass than water would. The viscosity of a material can be decreased with an increase in temperature in order to better suit an application | 52.5 mPa.s |
Additional Information
What are typical applications for ABChimie® 836 UV?
ABChimie® 836 UV is a UV-curable conformal coating designed to protect printed circuit board assemblies (PCBs) and components in demanding manufacturing environments, including:
- Automotive electronics (e.g., control units, sensors)
- Industrial automation (e.g., motor drives, PLCs)
- Consumer electronics (e.g., smart devices, wearables)
- Other high-reliability electronic assemblies
Learn More About ABChimie® 836 UV
ABChimie® 836 UV is a proven solution for engineers seeking fast, reliable protection of electronic assemblies in demanding manufacturing environments. This UV-curable conformal coating delivers rapid curing, excellent electrical insulation, and strong environmental resistance—ideal for applications in automotive electronics, industrial automation, consumer electronics, and other high-reliability assemblies.
Main Advantages of ABChimie 836 UV
ABChimie® 836 UV cures through a dual mechanism: UV exposure initiates rapid surface curing, while moisture ensures complete curing throughout the coating. This combination provides a uniform, durable protective layer with optimal adhesion and performance.
ABChimie® 836 UV provides excellent mechanical protection. This hardness helps resist scratches, abrasion, and minor impacts, ensuring long-term stability of encapsulated components.
ABChimie® 836 UV can be soldered through without generating highly toxic gases, ensuring safe processing while maintaining coating integrity.
ABChimie® 836 UV provides excellent adhesion even in harsh environments, forming a durable protective layer that resists moisture, chemicals, and temperature variations.
How to Choose a Conformal Coating
Selecting the most suitable resin requires consideration of key factors:
- ✔ Norms & Compliance
- ✔ Environment / Exposure Conditions
- ✔ Repairability
- ✔ Electrical Performance
- ✔ Application Method
- ✔ Operating Temperature
Compliance You Can Trust ✅
ABChimie® 836 UV meets stringent industry standards, ensuring reliability and regulatory adherence for OEMs and contract manufacturers:
- REACH Compliant
- RoHS 2011/65/EU Compliant
UL94 V0
UL746E (QMJU2-E308681)
Curing Tip: ABChimie 836 UV cures with UV rays. Use the appropriate equipment and recommended settings to achieve the best properties.
How to Optimise for the Best Results
PCBs must be completely dry and thoroughly clean, with no dust, grease, wax, or other contaminants. Coating adhesion depends directly on the quality of the substrate. All flux residues must be fully removed, as they can become corrosive and lead to circuit malfunctions.
For cleaning equipment or removing uncured ABChimie836UV or UV LED varnish, we recommend using SND or ABclean solvent.
It is essential to use the correct UV equipment (UV or LED) and follow the recommended settings to achieve the optimal properties of the cured conformal coating. ABChimie836UV and UV LED cure through UV exposure, with moisture contributing to a secondary curing mechanism.
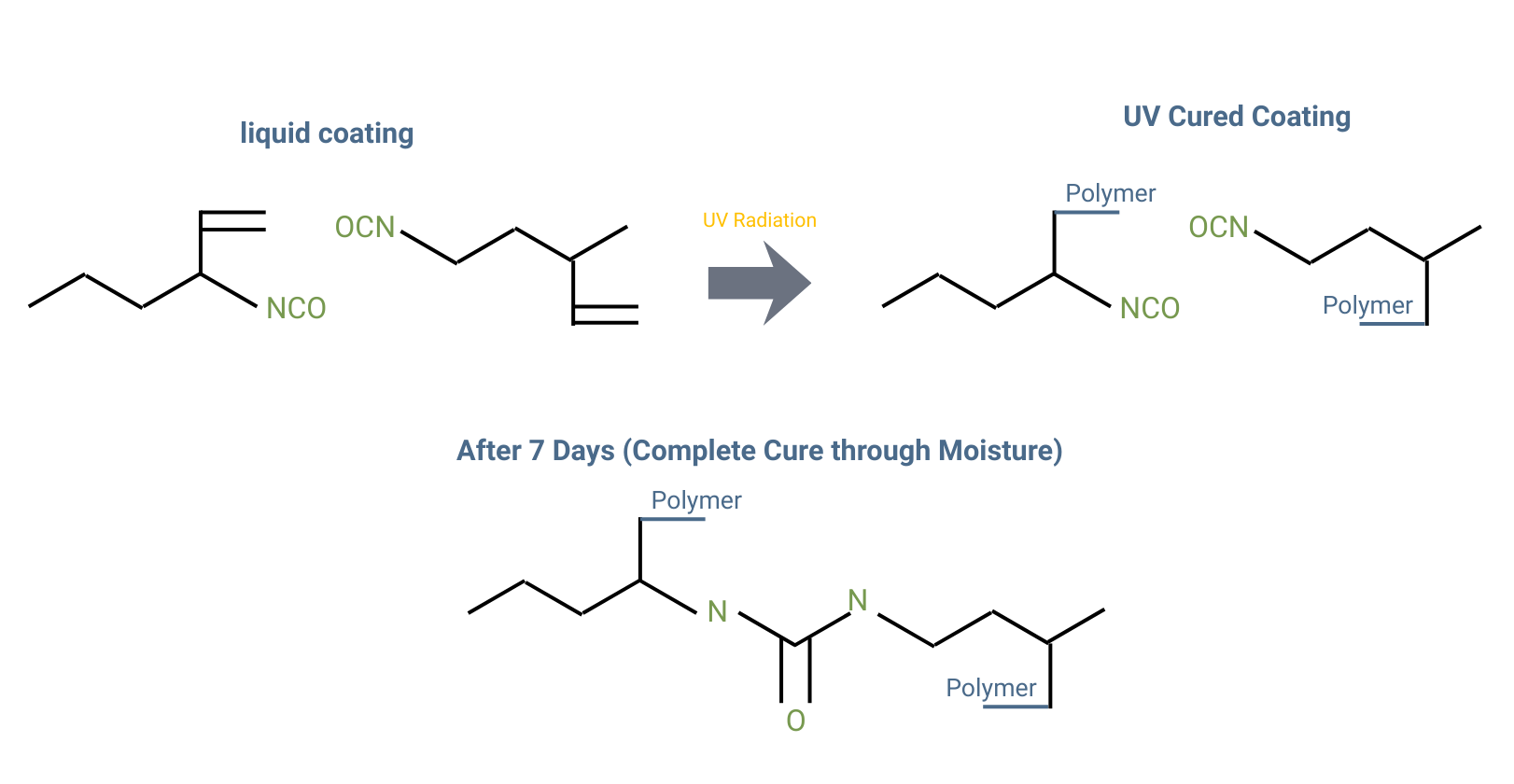
Curing Mechanism: UV light creates the first cure, and after 7 days the moisture from the environment completes the curing process.
How does Moisture Cure Work?
During UV curing, exposure to UV light activates the photoinitiators in the conformal coating, triggering rapid polymerization of the resin. This results in an immediate surface cure and fast development of handling strength. UV curing provides precise, on-demand curing in exposed areas, enabling high-throughput processing while maintaining coating uniformity.
ABChimie836UV and ABChimie836UV LED use the same dual curing mechanism to ensure complete curing, including in shadowed or hard-to-reach areas. Initial curing is achieved by UV exposure, while a secondary moisture-activated cure completes the process at ambient temperature. For full curing in shaded areas, a minimum relative humidity of 50% is required for at least 7 days.
Alternative to Mercury Lamp Curing of ABChimie 836 UV
ABChimie 836 UV is also available in the LED lamp version, which cures with an LED lamp.
ABChimie 836 UV LED [Go to 836 UV LED Product Page↗]
- Conformal Coating
- Fluorescent under UV light
- Excellent adhesion to flexible substrates
- Dual curing with UV LED exposure and moisture curing
Best suited for: High-speed process using LED light for curing




