EMI Materials
Electromagnetic interference occurs when the electromagnetic energy of one circuit interferes with another circuit.
To understand this, we must first talk about what electromagnetic energy is. When a device is plugged into electricity, it has voltage and current.
Voltage creates an electric field around the device.
Current (the flow of electricity) creates a magnetic field.
Together, these are called electromagnetic energy. This energy is always present when electricity flows, even in everyday devices like lamps, chargers, or computers.
As this energy spreads, it can travel through wires or even through the air. If another nearby device “picks up” this energy, it can disturb the normal operation of that device.
This disturbance is what we call electromagnetic interference (EMI).
EMI can cause multiple issues in electronics, including:
Device Malfunction
EMI can cause electronic devices to behave unpredictably or stop working temporarily. For example, a keyboard might type on its own, or a motor might start and stop erratically.
Signal Distortion
Electromagnetic interference can corrupt or weaken signals in communication systems. This can result in static on radios, dropped Wi-Fi connections, or blurry video signals.
Circuit Overload
Strong EMI can introduce extra current or voltage into circuits, potentially damaging components. Sensitive electronics, like medical devices or microcontrollers, are especially at risk.
Safety Hazards
EMI can disrupt critical systems, creating dangerous situations. Examples include interference with airplane navigation, automotive sensors, or medical monitoring equipment.
As electronic devices have become faster and more compact, the risk of electromagnetic interference (EMI) disrupting their operation has grown. EMI absorbers were developed as a solution to control unwanted electromagnetic energy, reducing noise and protecting sensitive circuits in high-performance electronics.
Anatomy of an EMI Absorber
EMI Absorbers are flexible composite sheets incorporating specialized magnetic particles and can be ordered with or without non-conductive pressure-sensitive adhesive (PSA). They help suppress EMI noise by absorbing electromagnetic energy inside and around electronic devices and assemblies.
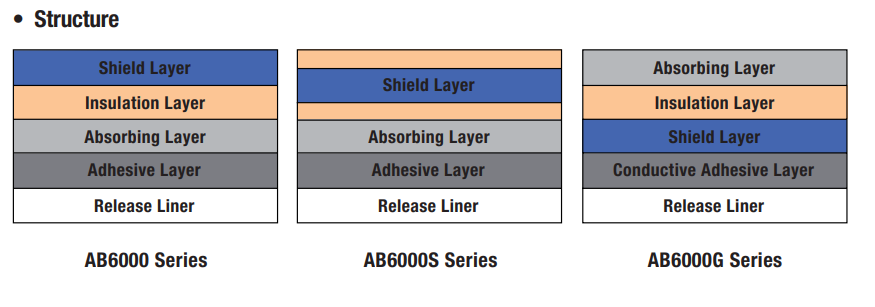
Shield Layer — Blocks or reflects incoming electromagnetic waves to provide the primary EMI protection.
Insulation Layer (optional) —Prevents electrical shorts while maintaining EMI control between conductive layers.
Absorbing Layer — Converts electromagnetic energy into heat, reducing reflections and lowering interference.
Adhesive Layer (optional) — Allows easy and secure attachment of the absorber to devices or enclosures.
Release Liner (optional) — A removable layer that protects the adhesive until the absorber is ready to be applied.
EMI Absorbers offer several structural and performance advantages that enable higher integration, better electrical performance, and improved efficiency:
Directly to the noise source
Attach directly to and/or opposite side of noise source (traces, cameras, digital IC's, chip, microprocessor)
Surfaces
Attach to the enclosure surface
Module Components
Insert between module components to help reduce coupling
Cables
Cable wrapping/attachment- round or flex cable
Where EMI Absorbers Deliver the Most Value
EMI Absorbers have become an essential solution for electronic systems that demand high signal integrity, low noise, and reliable performance as operating frequencies continue to increase.
They provide an effective balance between traditional shielding approaches and more complex mitigation techniques by absorbing and dissipating unwanted electromagnetic energy rather than reflecting it back into the system. This helps suppress radiated and conducted EMI, reduce crosstalk, and stabilize sensitive circuits without introducing additional interference paths.
By controlling electromagnetic noise at its source, EMI absorbers enable designers to improve system reliability and performance while avoiding the size, weight, and design constraints often associated with conventional metal shielding or over-engineered EMI solutions.
Primary driver: Signal integrity, reliability, and mission safety.
Suppression of radiated and conducted EMI that can disrupt radar, avionics, and communication systems
Protection of sensitive electronics from high-power RF, lightning strikes, and electromagnetic pulses (EMP)
Stable operation across extreme conditions (vibration, temperature, altitude) where shielding alone is insufficient
Primary driver: Cost, yield, and process scaling.
2.5D packaging provides the interconnect density needed to link:
- Compute, I/O, and memory chiplets
- Different process nodes within one package
- With bandwidth and latency comparable to monolithic dies
Primary driver: Signal integrity and I/O density.
2.5D integration allows:
- Switch cores, I/O chiplets, and retimers on one interposer
- Shorter interconnects and lower latency
- Improved signal quality at 400G, 800G, and beyond
Primary driver:
Signal integrity, reliability, and mission safety.
EMI Absorbers enable:
- Suppression of radiated and conducted EMI that can disrupt radar, avionics, and communication systems
- Protection of sensitive electronics from high-power RF, lightning strikes, and electromagnetic pulses (EMP)
- Stable thermal behavior in extreme operating environments
Key Features of EMI Absorbers
Excellent grounding with small contact areas, helping enable micro-electronic design.
Low electrical resistance/high adhesion helps provide reliable EMI shielding and grounding for a wide range of frequencies.
High performance on a variety of substrates for design versatility.
Can reduce the need to use a primer when bonding some LSE (Low Surface Energy) substrates.
Long-term performance at high temperatures (105ºC) for demanding applications.
High-performance in humid conditions for greater design flexibility.
CAPLINQ Solutions for Electromagnetic Interference
As electronic systems continue to increase in speed, density, and power, controlling electromagnetic interference (EMI) becomes a critical challenge. Without effective EMI management, unwanted electromagnetic energy can degrade signal integrity, reduce reliability, and compromise system performance.
EMI Solutions with 3M EMI Absorbers
Electromagnetic interference (EMI) management focuses on controlling unwanted electromagnetic energy, reducing noise, and protecting sensitive electronics from interference. The EMI absorber solutions below are commonly used in a variety of electronic systems and applications.
AB7000E Series
The 3M AB7000E Series EMI Absorber is a flexible polymer sheet loaded with soft metal flakes, designed for near-field EMI suppression from 300 MHz to 4 GHz, with optimal performance between 800 MHz and 2.5 GHz. It features a non-conductive acrylic pressure-sensitive adhesive for easy application (also available without adhesive) and is ideal for absorbing EMI inside and around electronic devices and assemblies.
AB8000 Series
3M EMI Absorber AB8000 Series is a high-temperature magnetic near-field EMI absorber material for electronic applications from
300 MHz to 4 GHz. The composite material features a silicone carrier resin for stable solder reflow and strong attachment to FPCs ,
along with magnetic fillers to suppress near-field EMI noise inside and around electronic devices and assemblies.
EM25TP Series
The 3M EM25TP Flux Field Directional Material is a magnetic composite with a carrier resin and magnetic fillers, designed for EMI absorption and magnetic shielding. It offers high permeability and magnetic loss to suppress EMI noise in its target frequency range (up to 15 MHz) and can prevent short circuits in electrical systems. With options like acrylic PSA for easy application and a black PET top film for durability, it’s ideal for custom high-performance stackups that efficiently couple and redirect magnetic fields.
AB60005SHF Series
The 3M AB6000HF/SHF Series is a hybrid EMI absorber combining a metal shielding layer and an absorbing layer separated by insulation. It provides high-frequency EMI shielding and noise suppression (up to 18 GHz) for improved signal-to-noise ratio, and features a pressure-sensitive acrylic adhesive with a removable liner for easy application. Available in sheets and rolls, it’s ideal for complex EMI control applications.

Phase Change Materials
Enable thin, uniform bondlines with stable thermal performance and minimal pump-out.
Thermal Putty Pads
Highly conformable materials designed to accommodate large tolerances and surface flatness variation.
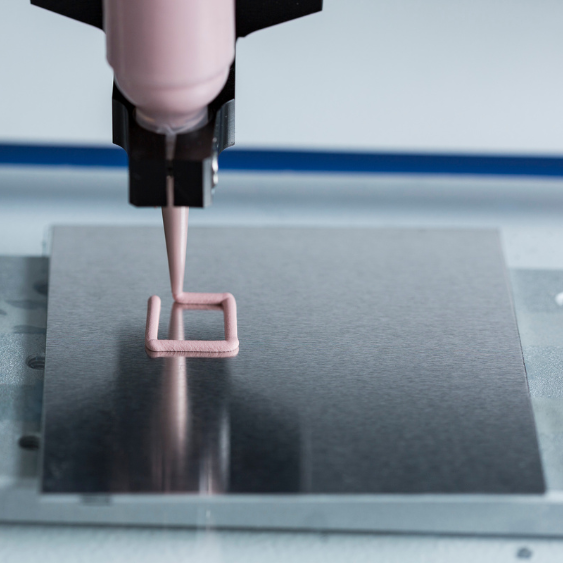
Thermal One-Part Hybrids
Dispense-ready materials supporting high throughput, long-term reliability, and reworkability.

Thermal Gap Pads
Compressible pads that provide electrical insulation and stress relief across uneven interfaces.

Thermal Grease
Easy-to-apply materials offering good initial performance but requiring pump-out validation.

Thermal Two-Part Hybrids
Dispensed systems combining softness, reliability, and long service life.

Why EMI Absorbers are Strong Candidates for High-Performance Electronic Systems
Among available EMI control solutions, hybrid and magnetic absorbers provide a practical balance between shielding effectiveness and design flexibility. They combine high-frequency absorption, magnetic field suppression, and predictable performance across varied geometries, while remaining compatible with complex assemblies and sensitive components.
In modern electronic systems, where high-speed circuits, dense layouts, and mixed-signal components can create localized EMI hotspots, these absorbers offer a way to maintain signal integrity, reduce noise, and protect sensitive electronics without compromising assembly design or reliability.
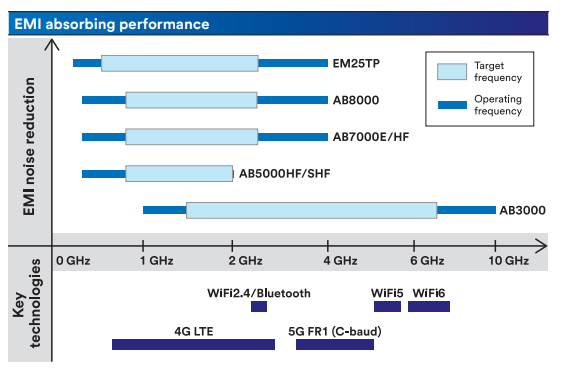
| 3M EMI Absorber Series | Frequency Range | Description |
|---|---|---|
| AB6000HF / SF Series | <18 GHz | Hybrid absorber for high-frequency EMI; combines metal shielding and absorbing layers; sheets and rolls; easy application with PSA |
| EM25TP Series | <15 MHz | Magnetic composite for EMI absorption and magnetic shielding; high permeability and magnetic loss; suitable for custom stackups; optional PSA and PET top film. |
| AB7000E Series | 300 MHz - 4 GHz (Optimal 800MHz - 2.5 GHz) | Flexible polymer with soft metal flakes; ideal for near-field EMI suppression; available with or without acrylic PSA. |
| AB8000 Series | 300 MHz - 4 GHz | High‑temperature magnetic near‑field absorber with silicone resin and magnetic fillers. |
For complex, high-speed electronic systems where EMI suppression, field uniformity, component sensitivity, and long-term reliability must all be balanced, hybrid and magnetic EMI absorbers provide a predictable and manufacturable solution that meets both performance targets and design constraints.
AB7000E SERIES
3M EMI Absorber AB7000E Series is an EMI suppression absorber for near-field applications from 300 MHz to 4 GHz Target
frequency range – or the optimal range for peak performance – is 800 MHz - 2.5 GHz. Consisting of a flexible polymer resin loaded
with a filler of soft metal flakes, this sheet is excellent for EMI absorption at frequencies from 300 MHz to 4 GHz.
An acrylic non-conductive, pressure-sensitive adhesive on one side makes application fast and easy, though this EMI absorber sheet is also available without adhesive. These sheet-type 3M EMI absorbers are great for absorbing near-field EMI inside and around electronic devices
and assemblies.
Key Features
- High permeability
- Broad operating frequency range from 300 MHz to 4 GHz
- Long shelf life (18 months)
- Broader temperature performance than AB7000HF Series
- Available with and without adhesive
- Multiple thicknesses available
- Release liner for easy handling
- Acrylic pressure sensitive adhesive
- Halogen free
Available Versions
- AB7050E-WO — 0.55mm thickness, 210 mm X 297 mm, without adhesive
- AB7020E-WO — 0.25 mm thickness, 210mm X 297 mm, without adhesive
- AB7010E-WO — 0.13mm thickness, 210mm X 297 mm, without adhesive
The following references provide practical guidance on product selection, and applications when using 3M EMI Absorbers as an RF/EMI management solution in advanced electronics assembly.
3M Electrically Conductive Tapes Selection Guide
3M material science and EMI/RFI management expertise
brings you a new conductive adhesive chemistry for
today’s demanding applications.
3M EMI/RF Shielding & Grounding Solutions
Summarizes the EMI and RF solutions available to protect various applications.
PTM6880
Solstice PTM6880 is a high-performance phase change material engineered for next-generation high-power semiconductor packaging. With a bulk thermal conductivity of 6.0 W/m·K and thermal impedance as low as 0.056 °C·cm²/W, it supports highly efficient heat removal in dense electronic assemblies where local heat flux and thermal gradients are significant. Its robust, non-pump-out formulation ensures stable interface behavior under aggressive thermal cycling and mechanical stress. Built on a polymer PCM system with optimized filler loading, PTM6880 has demonstrated reliability through 1000 thermal shock cycles and extended high-temperature aging, making it well suited for mechanically and thermally demanding package environments.
PTM6880 activates at a phase change temperature of approximately 45 °C, allowing the material to conform to surface irregularities, reduce interfacial resistance, and form extremely thin bond lines during operation. This combination of thermal efficiency and interface stability makes PTM6880 an effective choice for advanced, high-power packages where hotspot mitigation and long-term reliability are critical.
Thermal Impedance vs. Pressure
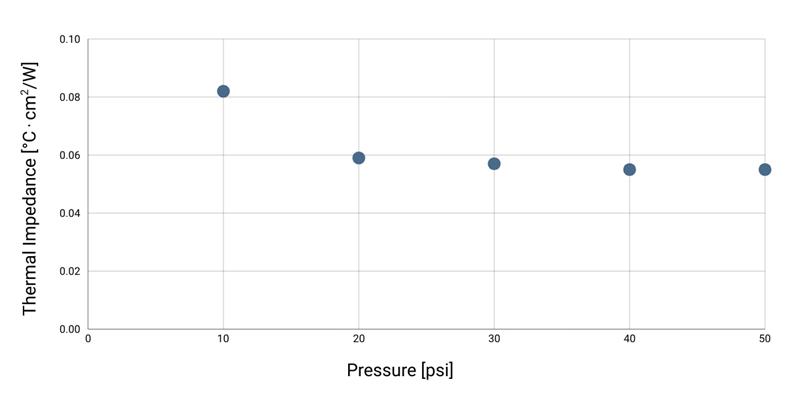
Typical thermal impedance values measured under controlled test conditions.
Key Material Properties (PTM6880)
0.056 °C·cm²/W (ASTM D5470)
6.0 W/m·K (ASTM D5470)
45 °C (DSC)
20 μm (Internal)
2.7 g/cm³ (ASTM D792)
Typical property values shown for reference only and should not be used as specifications.
For detailed specifications, application guidance, and background on PTM6880:
Controlling EMI with 3M Electrically Conductive Double-Sided Tape 5113DFT
3M Electrically Conductive Double-Sided Tape 5113DFT is an electrically conductive double-sided fabric tape (DFT) that provides
high adhesion, low electrical resistance, long shelf life, resistance to high temperature and humidity and excellent grounding and
shielding performance. It features a proprietary polyolefin XYZ-axis conductive pressure sensitive adhesive (CPSA) and a conductive
matrix carrier (a nickel/copper/nickel-coated conductive woven carrier).
This grounding tape provides excellent adhesion to a variety of substrates including metals and plastics and helps control signal
interference through passive intermodulation (PIM) mitigation for higher signal integrity and performance.
The following are the key features of 3M Electrically Conductive Double-Sided Tape 5113DFT:
Excellent EMI Shielding in Bond Line Gap
The material maintains strong EMI shielding effectiveness even within thin or uneven bond line gaps. This ensures continuous electromagnetic protection where traditional shields or gaskets may be less effective.
Excellent grounding with small contact areas for microelectronics
The material enables reliable electrical grounding even when contact areas are very small, as is common in miniaturized electronic designs. This makes it well suited for high-density microelectronics where space and contact geometry are limited.
Isotropic XYZ-axis conductivity through the adhesive
The adhesive provides uniform electrical conductivity in all directions, ensuring reliable grounding and consistent electrical performance across complex assemblies. This helps prevent signal discontinuities and improves overall EMI control.
Long-term performance at high temperatures (105 ˚C)
The material is designed to maintain stable electrical and mechanical performance during prolonged exposure to elevated temperatures. This ensures reliable EMI control and grounding in applications where thermal stress is a concern.
More Information About 5113DFT
Frequently Asked Questions About EMI Absorbers
What if I need a thicker absorber than what you offer?
A chiplet refers to a smaller, functional block of an integrated circuit. It either functions as a CPU, memory or as an input/output. In 2.5D packaging these chiplets are placed side-by-side and are connected to the interposer via microbumps.
Can EMI Absorbers be customised (ex. Higher frequency, different electromagnetic property, UL flame rating)?
2.5D packaging allows for heterogeneous integration and chiplet-focused approach, which means that package performance can be improved without being purely dependent on shrinking transistor sizes, which is restricted by both cost and physical limitations.
In what applications are EMI Absorbers most commonly used?
2.5D packaging is typically used for applications related to high-performance computing. AI accelerators, and high-end CPUs & GPUs. To cater towards increasing demand for HPC, improvements in 2.5D packaging are being developed such as silicon bridge solutions replacing the traditional silicon interposer, glass interposers & designing panel-level packaging.
Can EMI Absorbers work in extreme environments?
Traditional molding methods involve a pre-measured solid or semi-solid molding compound that is preheated, placed on an open mold cavity, then closed and compressed. On the other hand, liquid compression molding directly injects a liquid material into a heated mold. Traditional molding methods are preferred for larger, simpler packaging designs while LCM is preferred for more intricate, advanced packaging.
Further Reading on EMI Absorbers
Suppress electromagnetic interference and improve signal integrity in advanced electronic systems.
Talk to our engineers about selecting the right materials for your package architecture, thermal budget, and long-term reliability requirements.