HGP12 | High Thermal Conductivity Gap Pad
Technical Specifications
| General Properties | |
| Color Color The color | Pink |
| Film Thickness Film Thickness Film thickness is the thickness of a backing film without taking into account any coatings or adhesive layers. It is measured in micron and the conversion factor to mil is 0.039. | 0.5 - 2 mm |
| Specific Gravity Specific Gravity Specific gravity (SG) is the ratio of the density of a substance to the density of a reference substance; equivalently, it is the ratio of the mass of a substance to the mass of a reference substance for the same given volume. For liquids, the reference substance is almost always water (1), while for gases, it is air (1.18) at room temperature. Specific gravity is unitless. | 3.3 |
| Thermal Properties | |
| Thermal Conductivity Thermal Conductivity Thermal conductivity describes the ability of a material to conduct heat. It is required by power packages in order to dissipate heat and maintain stable electrical performance. Thermal conductivity units are [W/(m K)] in the SI system and [Btu/(hr ft °F)] in the Imperial system. | 12.0 W/m.K |
| Thermal Impedance | 0.13 °C·cm²/W |
| UL 94 Rating UL 94 Rating Flammability rating classification. It determines how fast a material burns or extinguishes once it is ignited. HB: slow burning on a horizontal specimen; burning rate less than 76 mm/min for thickness less than 3 mm or burning stops before 100 mm V-2: burning stops within 30 seconds on a vertical specimen; drips of flaming particles are allowed. V-1: burning stops within 30 seconds on a vertical specimen; drips of particles allowed as long as they are not inflamed. V-0: burning stops within 10 seconds on a vertical specimen; drips of particles allowed as long as they are not inflamed. 5VB: burning stops within 60 seconds on a vertical specimen; no drips allowed; plaque specimens may develop a hole. 5VA: burning stops within 60 seconds on a vertical specimen; no drips allowed; plaque specimens may not develop a hole | V-0 |
| Electrical Properties | |
| Volume Resistivity Volume Resistivity Volume resistivity, also called volume resistance, bulk resistance or bulk resistivity is a thickness dependent measurement of the resistivity of a material perpendicular to the plane of the surface. | 1.4x1013 Ohms⋅cm |
Additional Information
Frequently Asked Questions About HGP12 (12 W/m·K Ultra-Soft Thermal Gap Pad)
Learn More About HGP12 (12 W/m·K Ultra-Soft Thermal Gap Pad)
HGP12 is a high-conductivity, ultra-soft silicone gap pad designed to deliver efficient heat transfer while minimizing compression force on sensitive components. It offers low volatility, low siloxane content, and excellent wetting of uneven surfaces for stable long-term performance.
Key Features at a Glance
- ✔ 12.0 W/m·K thermal conductivity
- ✔ Ultra-soft, low-pressure compression
- ✔ Excellent interface wetting
- ✔ Low volatility & low siloxane
- ✔ High dielectric strength
- ✔ UL 94 V-0 equivalent safety rating
Versatile Application Methods
Application Methods
HGP12 is installed as a pre-cut pad placed directly between heat-generating components and heat sinks. Its softness enables hand placement or automated assembly without high clamping force.
Reliable Across Environments
Low volatile content and low oil bleed ensure stable performance in optical, telecom, and automotive environments sensitive to contamination.
Compliance You Can Trust ✅
HGP12 meets stringent safety, performance, and material compliance standards required for high-end electronics.
- UL 94 V-0 flame retardancy (equivalent)
- Low volatility per ASTM E595
- Low siloxane (D3–D10 < 100 ppm)
- High dielectric strength
- ASTM D5470 thermal performance validation
- ASTM D257 electrical insulation compliance
Applications That Benefit Most from High Thermal Conductive HGP12

Case 1: Improving Thermal Efficiency in High-Density 5G RF Amplifiers
5G telecom base stations rely on high-power RF power amplifier (PA) modules that generate significant heat densities. As module power output increases, maintaining thermal stability and preventing derating becomes a major design challenge which may results to thermal throttling.
Technical Issues:
- Hotspots of +18°C above average due to poor conformability
- Module derating occurred during extended high power operation
- Long-term reliability concerns (voiding, pump-out, bleed contamination)

High-power industrial LED fixtures such as those used in factories, warehouses, tunnels, and outdoor infrastructure operate continuously and generate significant heat at the LED junction. Excess heat leads to lumen depreciation, color shift, and premature failure, making efficient thermal management essential for maintaining long service life and consistent light output.
Technical Issues:
- LED junction temperatures exceeding design limits, causing early lumen drop-off
- Hotspot formation due to uneven metal-core PCB (MCPCB) surface contact
- Thermal grease dry-out over time leading to increased thermal resistance
- Long-term reliability concerns during 24/7 operation in hot or enclosed environments
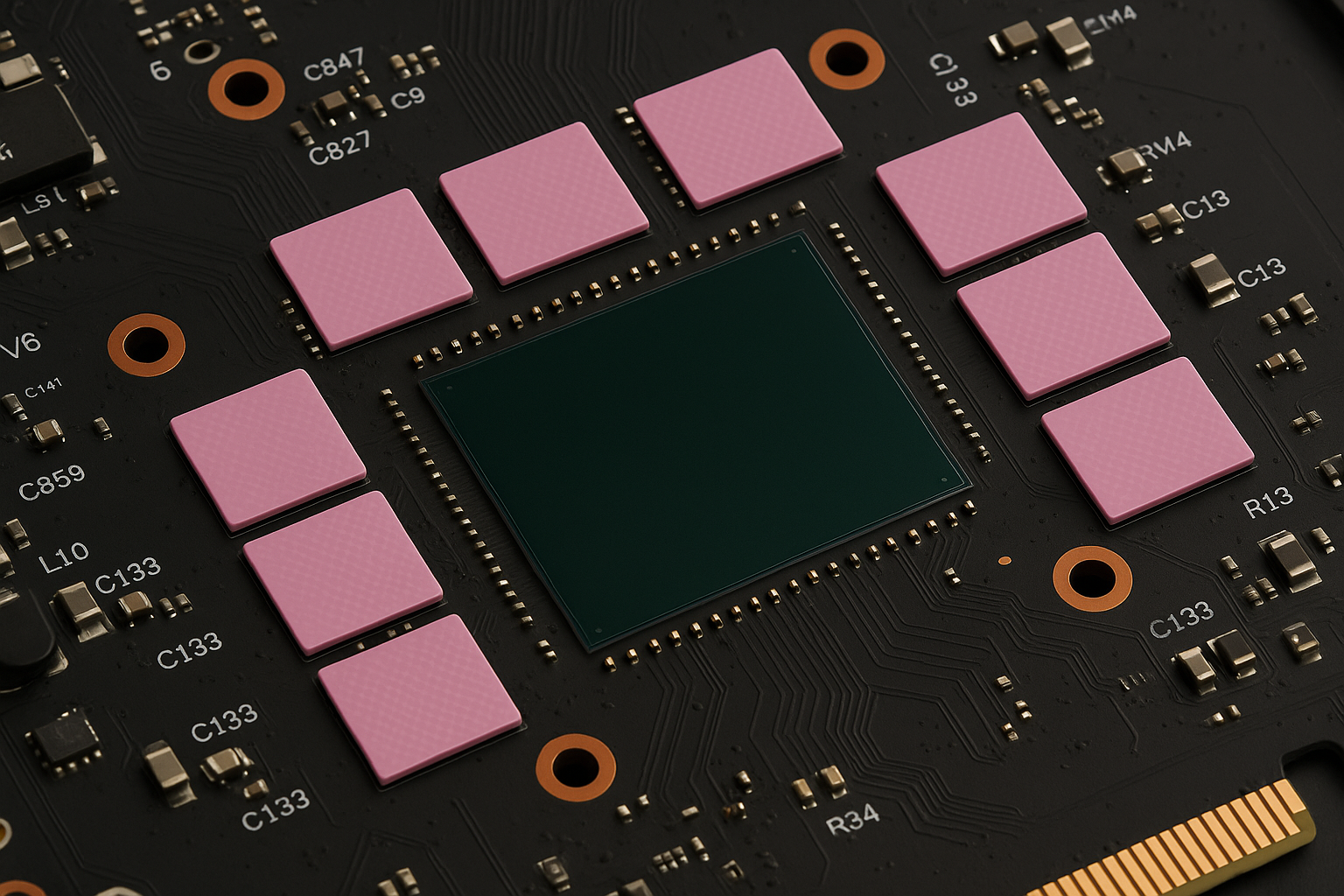
Modern AI training and inference servers use multi-die GPU accelerators that generate extreme heat fluxes, especially during sustained workloads. Maintaining low thermal resistance across complex module topographies is essential to prevent performance throttling and maintain system uptime in data centers.
Technical Issues:
- High heat flux (exceeding 300 W/cm²) from stacked GPU dies
- Gap variation due to tolerances in heat spreaders and interposers
- Performance throttling during extended ML training workloads
- Long-term aging concerns with traditional pads at elevated temperatures

Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) rely on high-power processors, radar modules, and sensor fusion units that operate continuously under harsh automotive temperature cycles. These compact modules generate high heat loads that must be controlled to prevent thermal throttling and loss of processing performance.
Technical Issues:
- Peak temperatures approaching thermal throttling threshold during continuous lane-assist operation
- Uneven PCB-to-housing gaps due to vibration and mechanical tolerances
- Traditional gap fillers showing micro-voiding after extended thermal cycling
- Risk of reduced processing speed and degraded ADAS reliability
How HGP12 Helps in These Cases
Solstice HGP12 provides a consistent thermal advantage across all the applications mentioned. Its high thermal conductivity of 12 W/m·K allows heat to move quickly away from critical components, helping to lower junction temperatures and prevent performance loss under heavy load. Overall, HGP12 supports reliable heat transfer, improves operational stability, and helps extend the lifetime of electronics that operate under high thermal stress.