Camera Module Assembly
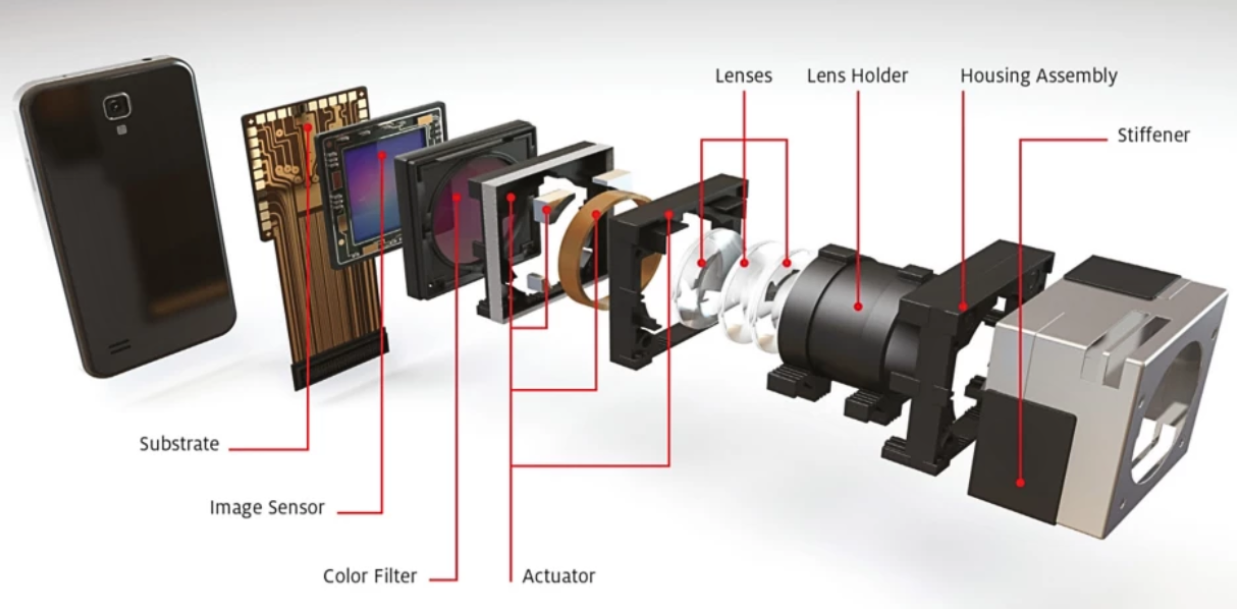
The modern camera module is far more than just a tool for taking photos; it's the core sensor that enables devices to see and understand the world. This tiny, integrated system is driving the next wave of intelligent technology across every industry.
From allowing your smartphone to recognize your face for secure payments, to guiding an autonomous vehicle safely through traffic, to inspecting micro-components on a factory floor, camera modules are the essential eyes of AI and machine vision. Their compact size and versatility make them essential components in a wide range of applications, including medical diagnostics, robotics, security, and consumer electronics.
Introduction: Advanced Adhesives for Camera Module Assembly
In the world of high-performance camera modules, success is measured in microns. As cameras become smaller, more powerful, and more complex, the role of advanced adhesives has evolved from simple bonding to a critical engineering component. At Caplinq, we offer a comprehensive portfolio of specialized adhesives tailored to meet the demanding requirements of every step in the camera module assembly process, ensuring precision, reliability, and manufacturability at scale.
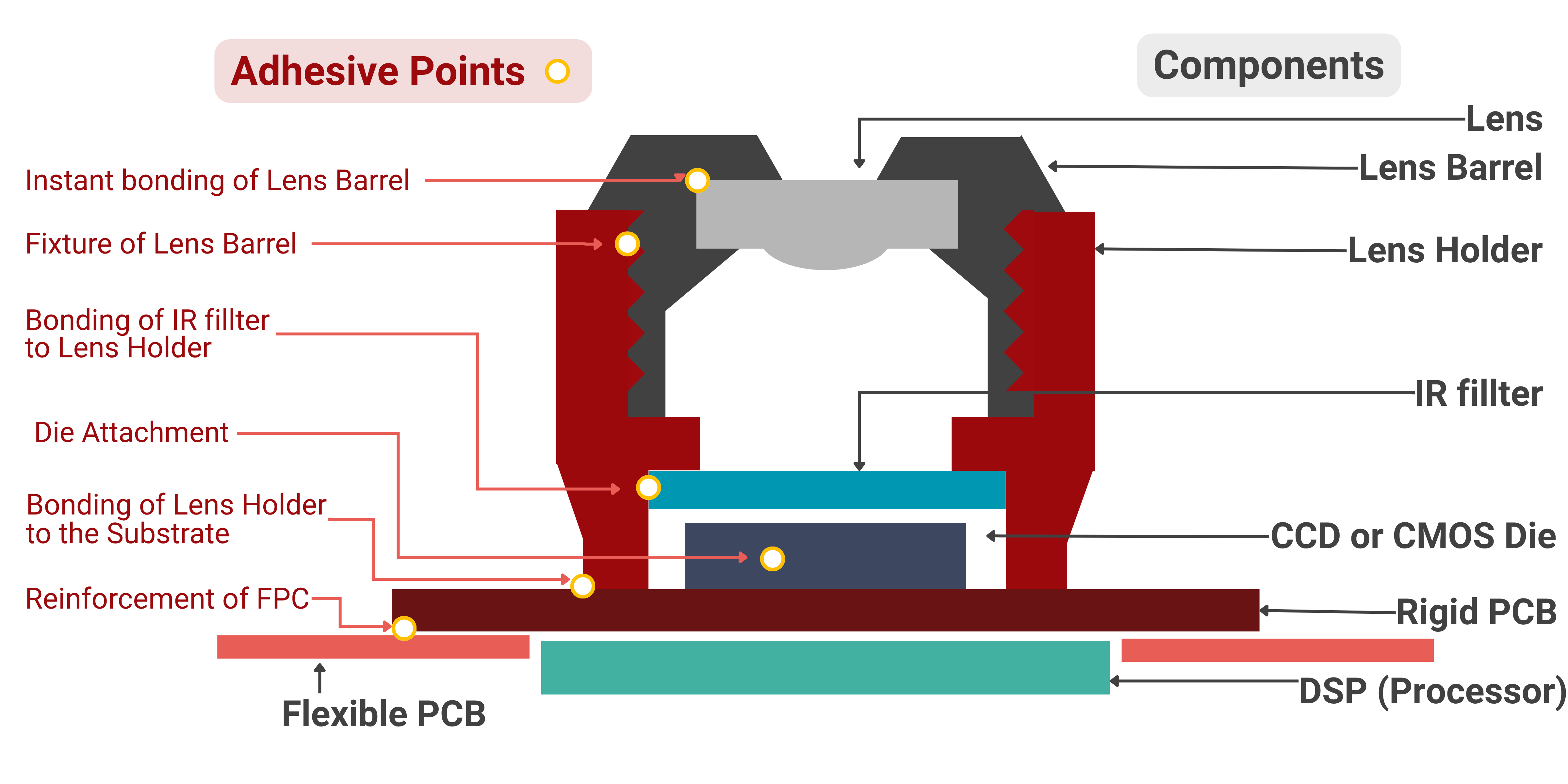
Components:
To achieve this level of intelligent vision, the phone’s camera module is built from several highly precise, integrated components:
Substrate & PCB
The foundation of the module. This circuit board (often FPC) provides electrical connection and mechanical support for all components.
Processor
The module’s “brain.” It processes raw data from the sensor, performing noise reduction, color correction, and sharpening.
Image Sensor
The digital film of the camera. A grid of light-sensitive pixels that converts light into electrical signals.
IR Cut Filter
A filter that blocks invisible infrared light, ensuring accurate and natural color capture in the final image.
Actuator
An electro-mechanical component (VCM) that moves the lens system for autofocus (AF) or Optical Image Stabilization (OIS).
Lenses
A stack of optical elements designed to gather light and focus it sharply onto the image sensor.
Lens Holder
Securely houses and aligns lens elements, maintaining precise optical positioning for consistent image quality.
Housing Assembly
The outer shell that protects the lens and actuator system, maintaining structural integrity and shielding from dust.
Stiffener
A metal shield providing extra protection and rigidity, safeguarding the module against physical damage and drops.
Camera Module Assembly Flow
The camera module is assembled through a sequence of precision processes to integrate the optical, electronic, and mechanical components. Each step ensures correct alignment, electrical connectivity, and mechanical stability for high-performance imaging in compact devices.
The Challenge: Pushing the Boundaries of Miniaturization
Modern camera module assembly presents a unique set of engineering challenges:
✅ Extreme Precision
Aligning optical components with sub-micron accuracy is essential for image quality. Even minimal misalignment can cause distortion, focus errors, or color fringing in high-resolution sensors.
✅ Component Protection
Delicate parts like lenses, sensors, and actuators must be protected from shock, vibration, and environmental stress. Structural design and encapsulation materials play key roles in maintaining stability and durability.
✅ High-Volume Manufacturing
Camera module assembly relies on automated lines where adhesives and bonding materials must cure within seconds. This ensures continuous throughput without sacrificing precision or quality.
✅ Long-Term Reliability
Each bond and mechanical joint must remain stable throughout the product’s lifespan, enduring years of temperature cycling, humidity, and mechanical stress without degradation in performance.
Our adhesives are engineered from the ground up to solve these challenges, enabling you to build the next generation of camera technology with confidence.
Our Adhesive Solutions: A Bond for Every Critical Joint
We offer a comprehensive suite of adhesives, each specifically tailored for a particular application within the camera module.
1. Bonding Lens Holder to Substrate
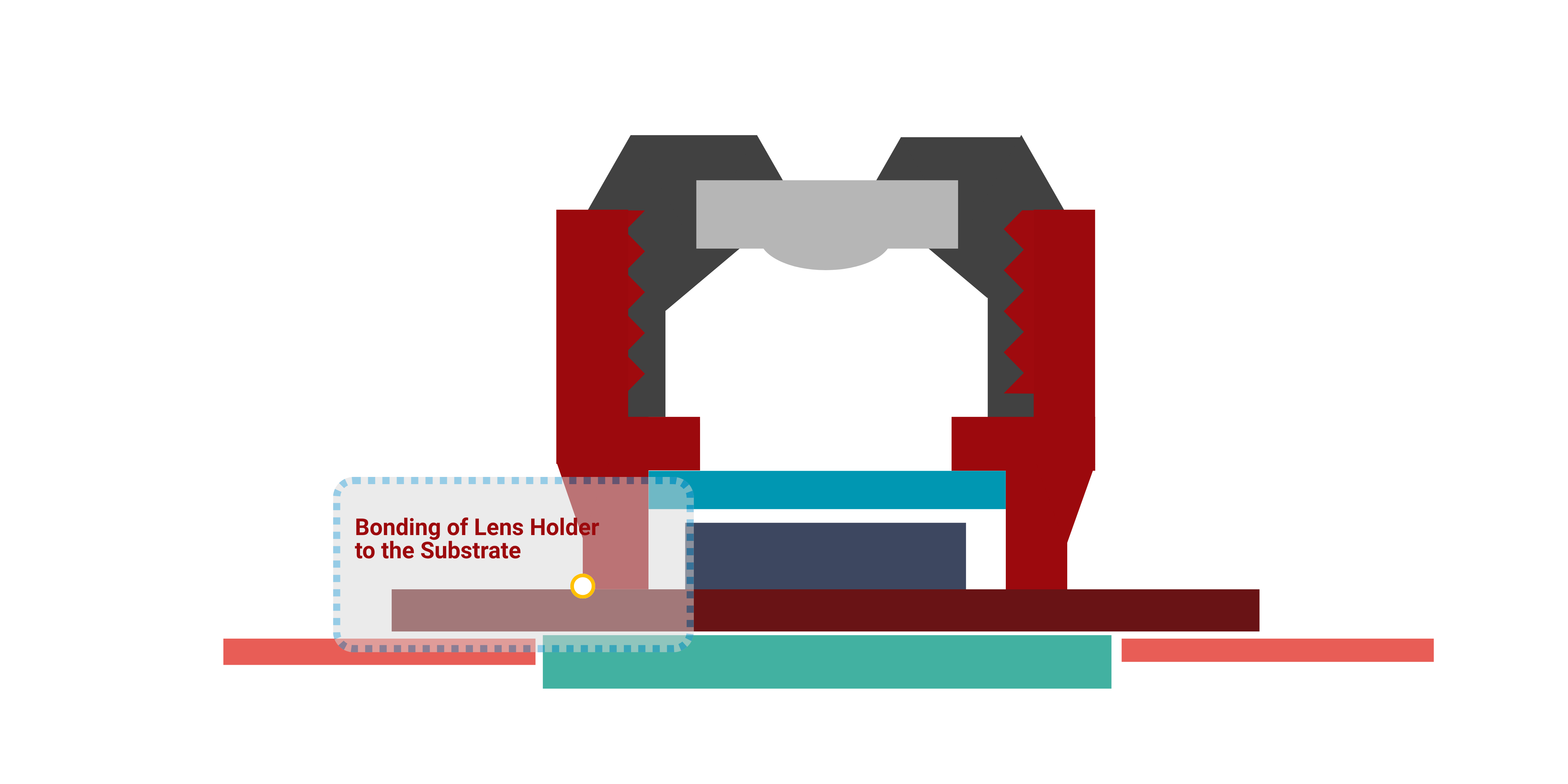
Active Alignment & House Assembly
This is the most critical bond for autofocus cameras. Our dual-cure (UV + Thermal) adhesives are the industry standard for active alignment, providing an instant UV "tack" to lock in perfect focus, followed by a full thermal cure for maximum structural strength and long-term reliability.
Key Properties:
- Ultra-low shrinkage
- Excellent adhesion to LCP/PC plastics and FR4
- High reliability
2. Lens & Barrel Assembly
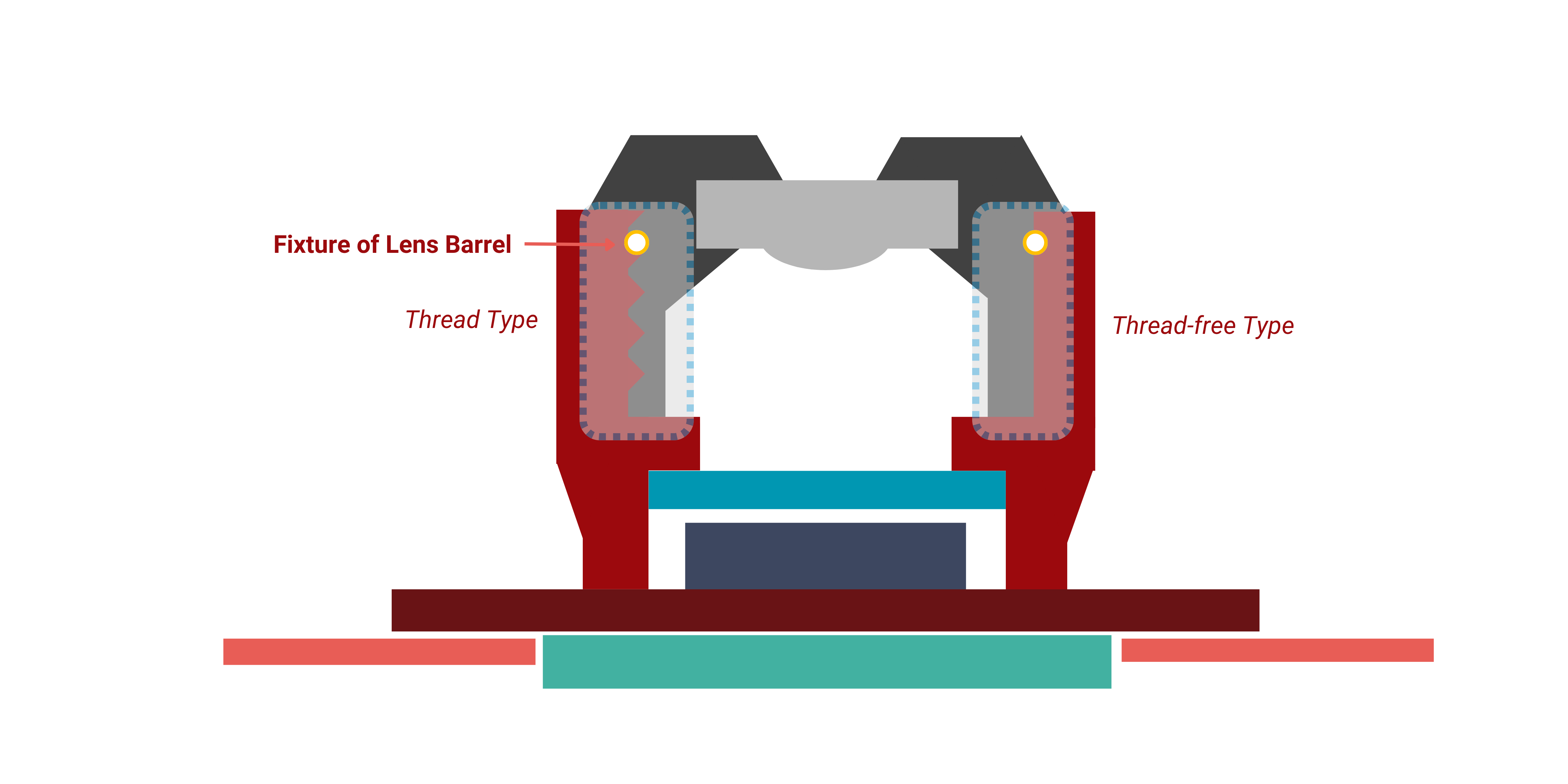
Lens Locking, Lens Bonding, IR Filter Sealing
For the assembly of the core optical unit, our one-step UV-cure adhesives provide the speed and precision required. They create stress-free bonds that protect the delicate lenses and form a perfect, contaminant-free seal. Some designs require low-temperature curing epoxy.
Key Properties:
- Rapid "snap cure" (1–3 seconds)
- Low outgassing, high thixotropy (no-flow)
- Excellent optical clarity, high viscosity
Henkel’s Solutions: Active Alignment
The table below summarizes Henkel’s UV+Thermal Dual-Cure and UV-Cure Adhesives designed for active alignment processes in optical assemblies.
| Properties | Testing Items | NCA 2286 ★ | NCA 2286AE ★ | NCA 2390 ★ | NCA 3217 | NCA 01UV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transmittance | UVT, 200 µm, 400–750 nm wavelength, % | 6–20% | 2–10% | 15–30% | Black | White |
| Typical Curing Conditions (365nm) | – | 4 s @ 100 mW/cm² 60 min @ 80°C | 4 s @ 100 mW/cm² 60 min @ 80°C | 3 s @ 1000 mW/cm² 30 min @ 80°C | 1 s @ 100 mW/cm² (220–260 nm) 30 min @ 60°C | 3 s @ 1000 mW/cm² |
| Viscosity | 20 mm 2°, con/plate, 2 s⁻¹, 25°C, mPa·s | 43,000 | 46,000 | 55,000 | 37,600 | 27,000 |
| TI | – | 5.7 | 5.7 | 5.2 | 2.9 | 5.6 |
| Cure Depth | 2×1500 mW/cm² | 0.45 | 0.40 | NA | / | 8 |
★ Highly Recommended
CAPLINQ Solutions: Active Alignment
The table below summarizes CAPLINQ UV+Thermal Dual-Cure and UV-Cure Adhesives designed for active alignment processes in optical assemblies.
| Products | EO-934CM | EO-474CM | EO-454CM | JD786-6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Appearance / Color | Liquid / Gray | Gray or Milky Yellow | Milky White or Slightly Blue-White | Black |
| Viscosity (25°C, 514.20 rpm) | 20,000–40,000 | 28,000–43,000 | 22,000–38,000 | 22,400–30,460 (514.3 rpm) |
| Thixotropic Index | 2.4 | 2.8 | 3.2 | 3.0 |
| Pot Life (25°C) | 3 days | 3 days | 3 days | 3 days |
| UV Wavelength (nm) | 310–365 | 310–365 | 310–365 | 310–365 |
| Curing Light Energy (mj/cm²) | 3,000–6,000 | 3,000–6,000 | 3,000–6,000 | 3,000–6,000 |
| Post Cure (Heat) | 120°C, 30 min | 120°C, 60 min | 130°C, 10 min | 130°C, 10–30 min / 80°C, 60–90 min |
| Glass Transition Temp. Tg (°C) | 148 | 149 | 151 | 149 |
| CTE (α1/α2) | 37 / 82 | 37 / 86 | 37 / 80 | 37 / 82 |
| CTE (°C, Tg μm/m°C) | 189 / 160 | 189 / 160 | 189 / 160 | 189 / 160 |
| Specific Gravity | 1.22 | 1.21 | 1.23 | 1.26 |
| Hardness (Shore D) | 80 | 82 | 82 | 82 |
| Water Absorption (25°C, 24h) | 0.47% |
3.1 Structural & FPC Reinforcement
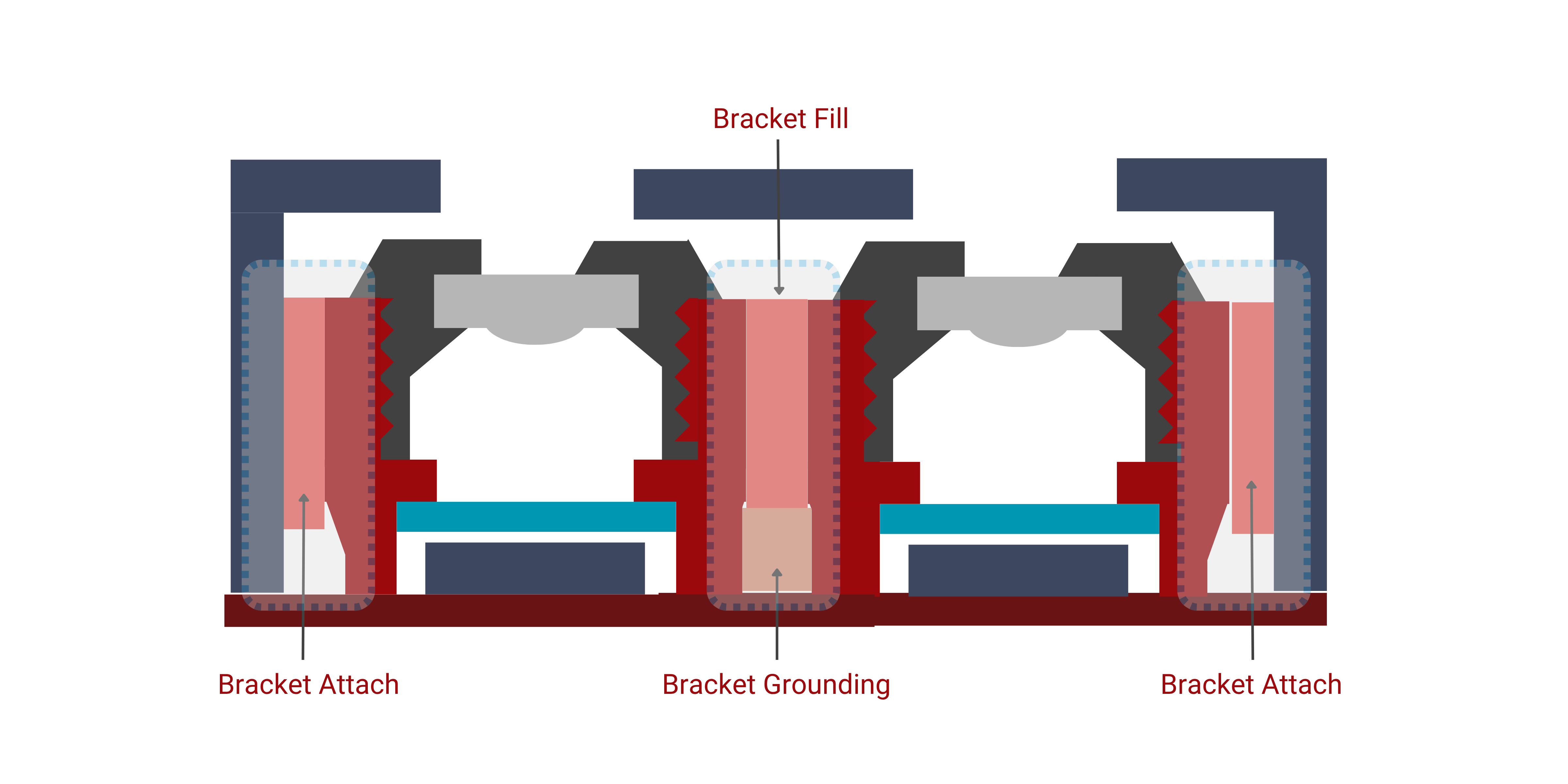
Bracket Fill
Bracket Fill (also called Side Fill) is the process of dispensing a specialized adhesive into the tiny gaps between the fully assembled camera module and its surrounding metal bracket or shield.
Key Properties:
- Low viscosity & excellent flow
- Low-temperature cure
- High adhesion strength
- Controlled modulus (toughness) to absorb impact energy without cracking
3.2 Structural & FPC Reinforcement
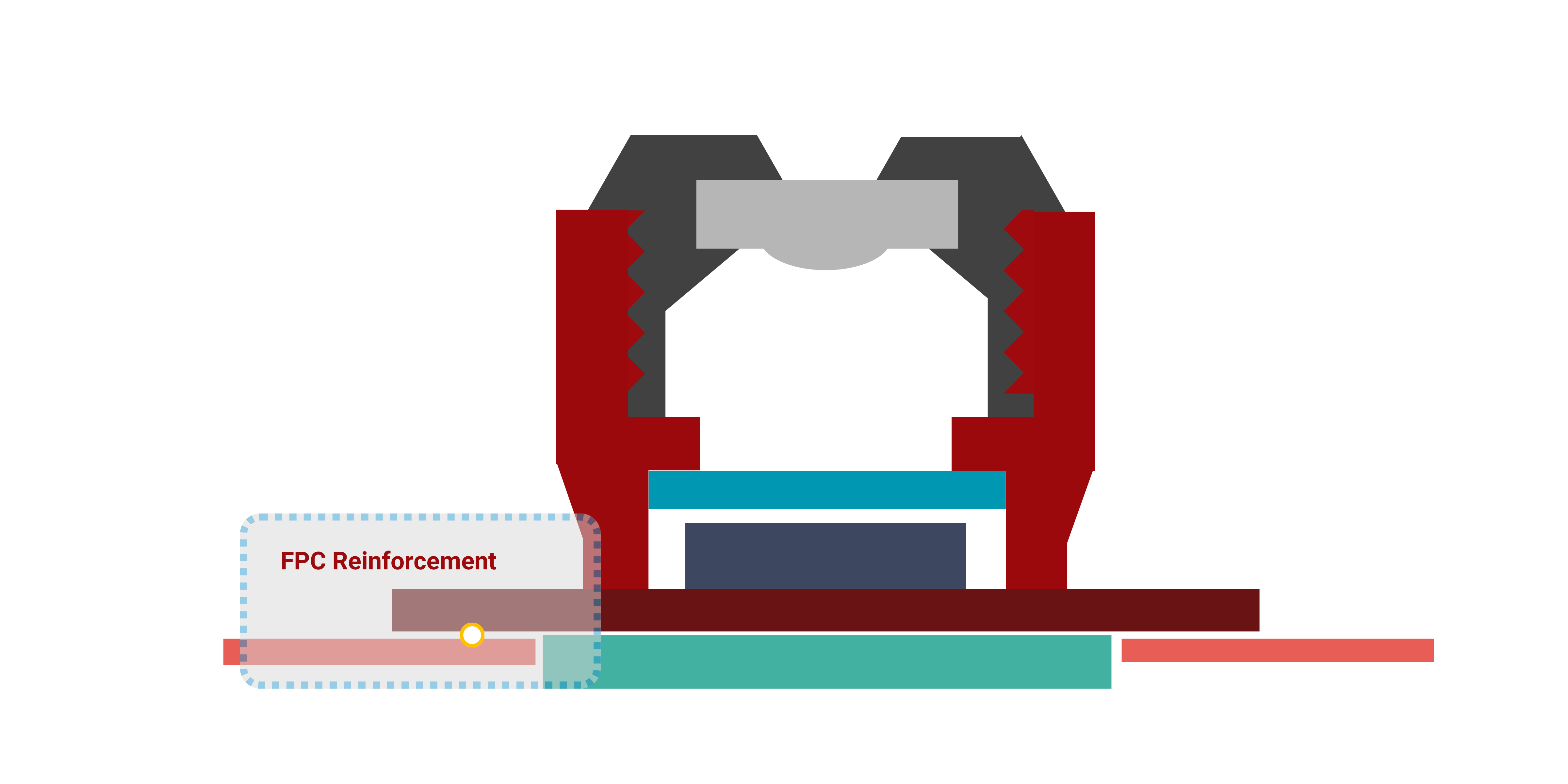
Flex Attach
To ensure durability against drops and impacts, our gap-filling epoxies and flexible adhesives provide critical structural reinforcement. They absorb shock, dampen vibration, and protect the fragile FPC connection points from tearing or cracking.
Key Properties:
- Low viscosity for excellent gap-filling (Bracket Fill)
- High flexibility and fatigue resistance (FPC Reinforcement)
Henkel’s Solutions: UV-Cure Adhesive
The table below summarizes Henkel’s UV+Thermal Dual-Cure and UV-Cure Adhesives designed for Lens Locking, IR Filter to Lens Housing / FPC Reinforcement.
| Property | LOCTITE 3703 | LOCTITE AA 3106 |
|---|---|---|
| Appearance (uncured) | Beige translucent paste | Transparent to slightly hazy liquid |
| Cure Conditions | UV: 80s @ 30mW/cm² (365nm) | UV: 80s @ 30mW/cm² (365nm) |
| Viscosity (cP) | 18,000–35,000 | 3,500–7,500 |
| Key Substrates | Rigid/Flexible PVC to Polycarbonate, Glass, many plastics, most metals | Polycarbonate, Glass, many plastics, most metals |
| Tensile Strength (N/mm²) | 13.8 | 25.0 |
| Elongation (%) | 85 | 250 |
| Shore Hardness (D) | 40 | 36 |
| Glass Transition Temp (°C) | N/A | N/A |
| Specific Gravity | 1.12 | 1.078–1.08 |
| Operating Temperature Range | – | -54°C to +149°C |
| Water Absorption (%) | N/A | 3.18% (2h in boiling water) |
★ Highly Recommended
CAPLINQ Solutions: UV Cure Adhesive
The table below summarizes CAPLINQ's UV-Cure Adhesives designed for Lens Locking, IR Filter to Lens Housing / FPC Reinforcement.
| Products | AO-717MT | AO-305CM | AO-329PL |
|---|---|---|---|
| Color | Colorless | Transparent | Blue |
| Viscosity 25°C (cps) | 200–400 | 13,000–20,000 | 4,700–7,200 |
| Thixotropic Index | Not specified | Not specified | ≥5.5 |
| Refractive Index | 1.4753 @25°C | Not specified | Not specified |
| Hardness (Shore D) | 75±2 | 59 | 44 |
| Glass Transition Temp. (Tg) (TMA) | Not specified | 38.36°C | 47°C |
| CTE α1 / α2 (ppm/°C) | Not specified | 108.2 / 454.5 | 65 / 218 |
| Water Absorption (25°C/24hr) | Not specified | 2.47% | 2.80% |
| Recommended Curing (nm) | 365 nm | 365 nm | 365 nm |
| Post-cure (Heat) | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Shelf Life | 8 months | 25°C | 9 months (14–34°C) |
| Application | Bonding PC, ABS, PC electroplating for aluminum, iron, and stainless steel | Focusing and fixing CMOS module plastic lens holders | Focusing and fixing lenses to lens holders |
| Alternatives | LOCTITE ECCOBOND DS 3318LV | LOCTITE 3703 | LOCTITE AA 3106 |
4. Die Attach and Underfill
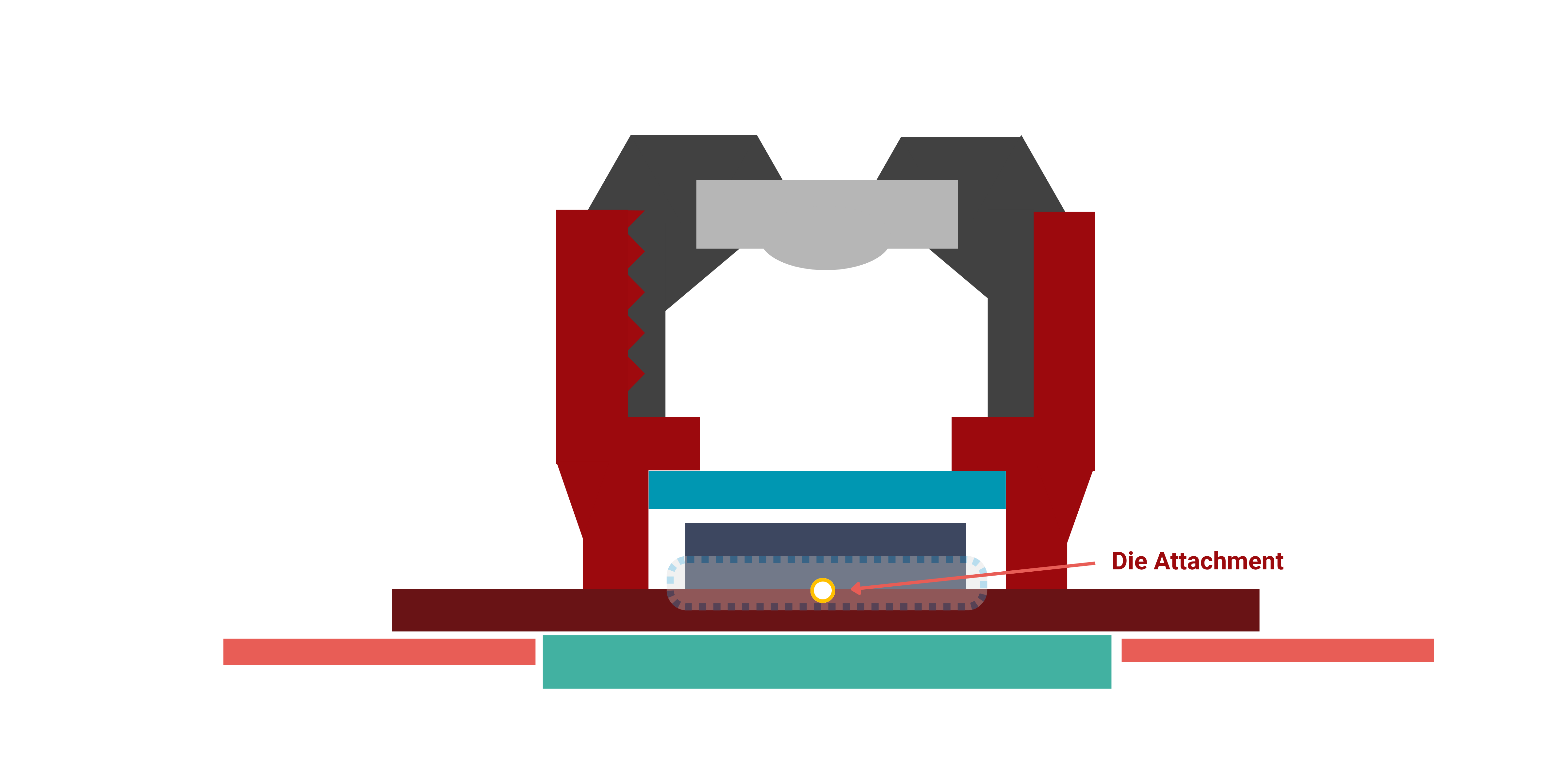
Bonding Image Sensor to Substrate
The foundation of the module requires a stable, reliable bond. Our thermally conductive die-attach adhesives provide a rock-solid foundation for the image sensor while efficiently pulling away heat, which is critical for maintaining high image quality. Our Underfill can ensure bump reinforcement and protect the connection of the camera module to the PCB during reliability testing and in use.
Key Properties:
- High thermal conductivity, low-temperature cure, and excellent reliability
- Underfill with high thixotropic index, controlled flow, good bump coverage, and good fillet capability
5. VCM (Voice Coil Motor) Assembly
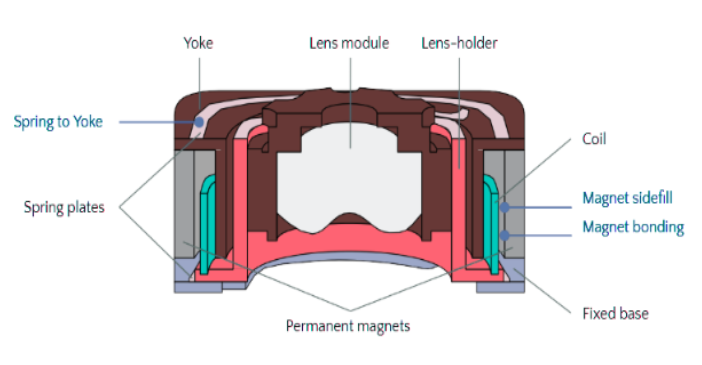
The assembly of the autofocus motor requires robust, precise bonding. Our structural adhesives provide the exceptional strength needed to secure magnets and delicate springs, ensuring flawless and reliable motor performance over billions of cycles.
Key Properties:
- High bond strength
- high thixotropy
- low-temperature thermal cure to protect sensitive components.
UNDERFILL SOLUTIONS
Capillary Flow and No Flow. Featured Underfill Solutions for Camera Module Assemblies
LOCTITE ECCOBOND E 1216M ↗
Capillary flow, low-viscosity underfill with strong adhesion and good reliability for delicate optical assemblies.
- Viscosity: 4,000 cP – designed for rapid capillary flow under dies and lenses
- Tg of 125°C with a CTE below Tg of 35 ppm/°C ensures stability under moderate thermal cycling
- High modulus (7,600 MPa) provides strong mechanical support to solder joints
- Ideal for compact camera modules and consumer optical sensors requiring fast flow and clean fill
LOCTITE ECCOBOND FP 5201 ↗
No-flow underfill designed for thermal compression bonding and advanced packaging reliability.
- Viscosity: 21,000 cP (5 rpm) for controlled dispensing and no-flow operation
- High glass transition temperature (171°C) for superior heat resistance
- Moderate modulus (5,800 MPa) provides flexibility under stress and temperature variation
- Best suited for fine-pitch optical module components with tight process control and reflow compatibility
LOCTITE ECCOBOND NCP 5209 ↗
Non-conductive no-flow underfill formulated for thermal compression bonding in fine-pitch optical components.
- Viscosity: 12,500 cP (5 rpm) balances flow and placement precision
- Tg of 145°C and low CTE below Tg (28 ppm/°C) minimize stress in camera sensor interfaces
- High modulus (7,300 MPa) and stable mechanical strength at room temperature
- Recommended for advanced camera module designs requiring dimensional accuracy and mechanical rigidity
Henkel Solutions: Thermal Cure Adhesive
The following table compares Henkel’s thermal-cure epoxy and hybrid adhesives for housing and IR filter assembly applications.
| Testing Items | Unit | Loctite 3128 ★ | NCA 3220 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chemistry | – | Epoxy | Epoxy |
| Viscosity @ 5rpm | cps | 22,000 | 7,000 |
| TI, 0.5/5rpm | – | 3.2 | 3.3 |
| Worklife @ 25°C | days | 3 | 14 |
| Snap Cure @ 80°C | min | >5 | >4 |
| Oven Cure | – | 80°C @ 30 min | |
| Elongation @ break | % | 2 | 70 |
| Tg by TMA | °C | 45 | 26 |
| CTE by TMA, a1/a2 | ppm/°C | 40/130 | 61/171 |
| Modulus @ 25°C | MPa | 4,839 | 3,240 |
| Adhesion @ 25°C | MPa | 8.2 | 13 |
| Application | – | Holder Attach | Holder Attach |
| Volumetric / Linear Shrinkage on Cure | % | 1.0 (Linear) | 4.1 / 1.3 |
| Hardness Shore D | – | 88 | 79 |
★ Highly Recommended
Caplinq Solutions: Thermal Cure Adhesive
The following table compares CAPLINQ's thermal-cure epoxy and hybrid adhesives for housing and IR filter assembly applications.
| Property | Unit | EO-601CM | EO-585CM | LINOBOND EO-322PL |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Application | - | Suited for memory cards, CMOS assembling | Suited for memory cards, CMOS assembling | Memory cards, CCD/CMOS Assemblies |
| Chemistry Type | - | Epoxy 1K | Epoxy 1K | Epoxy 1K |
| Color | - | Black | Black | Black |
| Viscosity @25°C (514.50 rpm) | cps | 17,000–21,000 | 16,000–22,000 | 19,000–25,000 |
| Thixotropic Index | - | 4.5–5.5 | ≈3.4 | ≈2.3 |
| Pot Life @25°C | hours | 72 | 72 | 6 |
| Storage Temperature | °C | -20°C to -5°C | -40°C to -5°C | -20°C to -5°C |
| Storage Life | months | 6 | 6 | 6 |
| Initial Cure | min @ °C | 6 min @ 80°C | 60 min @ 80°C | 60 min @ 80°C |
| Full Curing Conditions | min @ °C | 15 min @ 80°C / 2 min @ 150°C | 50 min @ 80°C / 5 min @ 150°C | 30 min @ 120°C |
| Tg (TMA) | °C | 44 | 68 | 130 (DSC) |
| CTE α1 / α2 | ppm/°C | 37 / 178 | 83 / 229 | 66 / 178 |
| Hardness | Shore D | 80 | 82 | 82 |
| Shear Strength @25°C | N/cm² | 200 | 250 | N/A |
| Weight Loss (150°C) | % | <0.5 | <0.5 | <0.5 |
| Water Absorption (24H, 25°C) | % | 0.45 | 0.4 | 0.23 |
| Alternative | - | NCA 2360, Loctite 3128 | Loctite 3128 | – |
Die Attach Solutions
The following table lists our die attach solutions best for camera assemblies.
| Testing Items | Unit | 2035SC |
|---|---|---|
| IBOA Free | – | No |
| Warpage Performance (µm) | µm | >7 |
| Color | – | Black |
| Viscosity @ 5rpm (cps) | cps | 11,000 |
| TI, 0.5/5rpm | – | 3.1 |
| Worklife @ 25°C (days) | days | 3 |
| Oven Cure | hr | 1 hr @ 80°C |
| Young’s Modulus | MPa | 1,600 |
| CTE 25–125°C (ppm/°C) | ppm/°C | 43 |
| Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) | W/m·K | 0.17 |
★ Highly Recommended
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS ABOUT CAMERA MODULE ADHESIVES
Dual-cure adhesives provide an immediate UV "tack" that locks components in perfect focus almost instantly, allowing for precise optical alignment. The subsequent thermal cure ensures full mechanical strength and long-term stability, preventing shift during later processing or use. This two-step cure method balances speed, accuracy, and durability critical for autofocus camera modules.
What factors determine the choice between UV-cure and thermal-cure adhesives in optical component bonding?The selection depends on substrates involved, curing speed required, heat sensitivity of components, and bond strength needed. UV-cure adhesives offer rapid fixation and are ideal for transparent materials where optical clarity is essential. Thermal-cure epoxies deliver superior mechanical strength and reliability, especially where heat resistance and structural reinforcement of non-transparent parts are required.
How do adhesives contribute to the shock and vibration resistance of compact camera modules?Adhesives with controlled modulus and high flexibility absorb impact and dampen vibrations, protecting delicate lenses, image sensors, and actuators from mechanical stress. Gap-filling and flexible adhesives reinforce fragile flexible printed circuit (FPC) connections and bracket fills, improving overall robustness against drops without compromising miniaturization.
High thermal conductivity adhesives efficiently dissipate heat generated by the image sensor and processor, maintaining optimal operating temperatures. This prevents thermal noise and sensor degradation, which can adversely affect image quality. Choosing die attach adhesives with balanced thermal and mechanical properties ensures reliability and performance in high-resolution modules.
Can adhesives be customized to meet different camera module manufacturing throughput demands?Yes, adhesive formulations can be tailored for cure speed, viscosity, and pot life to align with automated production line speeds and process conditions. Fast UV curing supports high-volume throughput, while thermal curing parameters optimize mechanical strength without bottlenecking assembly. Custom adhesive solutions help manufacturers sustain precision and quality at scale.
What are the critical parameters for optimizing the UV + thermal dual-cure adhesive process during lens holder bonding?
Critical parameters include UV intensity and exposure time to ensure instant tack without overheating, followed by optimized thermal curing temperature and duration to achieve full cross-link density. Minimizing adhesive shrinkage and controlling coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) mismatches between adhesive and substrates are vital to maintain sub-micron optical alignment precision.
Related Blogs

Electrically Conductive Adhesives for Heat-Sensitive Electronics and Camera Modules
Learn how electrically conductive adhesives provide reliable electrical and mechanical bonding in heat-sensitive applications such as compact camera modules, sensors, and flexible electronics.




