Sealants, CIPG & FIPG
Sealants are specialized compounds engineered to create effective barriers against environmental elements, playing crucial roles in various industries. These versatile materials offer tailored solutions for sealing applications across construction, automotive, manufacturing, and electronics sectors. Designed with specific characteristics to meet diverse needs, sealants vary in composition to address varying requirements, from high-temperature resistance to flexibility and adhesion in dynamic environments. Our extensive selection includes cutting-edge sealing technologies and methods such as hotmelt PA, Specialty hotmelt, water-based, Butyl, Epoxy, Acrylic (MMA), SMP, PUR, and Hotmelt PSA. Whether you require anaerobic, silicone, polyurethane, or UV curing options, our comprehensive lineup ensures that you can find the ideal sealant for your application.
Formulated to withstand harsh conditions, sealants provide reliable bonding and sealing capabilities in construction projects, ensuring structural integrity and protection against moisture, dust, and contaminants. In automotive applications, they contribute to assembly processes by creating tight seals and preventing leaks in critical components such as engine parts and transmission housings. With their ability to conform to irregular surfaces and resist temperature variations, sealants play a vital role in ensuring the longevity and performance of products and structures across industries.
Product Selector Guide
Hotmelts Product Selector Guide
| Product | Application | Curing mechanism | Temperature resistance | Tensile strength (mPa.s) | Elongation (%) | Product features |
| BS-1000 V8 | Sealing / Gasketing | No curing | -40 - +60C | - | - | High-performance multipurpose adhesive/ sealant |
| BS-1950 V9338 | Sealing / Gasketing | Foaming | up to 180C | 0.008 | 220 | High set speed with balanced properties of resiliency, adhesion and operational temperature range |
Gaskets Product Selector Guide
| Product | Application | Curing mechanism | Viscosity (mPa.s) | Foam ratio (%) | Tensile strength (kPa) | Elongation (%) | Product features |
| BS-8000 V460 | Sealing / Gasketing | UV curing | 28,000 | 66 | 85 | 70 | Flexible and high heat resistance |
Frequently Asked Questions
Frequently asked questions about Sealants
What are sealants, and what role do they play in various industries?
Sealants are specialized materials designed to create effective barriers against environmental elements, serving critical roles in construction, automotive, manufacturing, electronics, and more. They provide reliable bonding and sealing capabilities, ensuring longevity and performance in diverse applications.
What are Hotmelt Sealants?
Hotmelt Sealants are thermoplastic adhesives commonly used in various industries. They exhibit low to medium viscosity at dispensing temperatures, solidifying upon cooling to create robust bonds. Their properties include versatility in physical states, excellent durability, resistance to moisture, chemicals, oils, and temperature extremes.
What temperature does the hot melt glue work?
Hot melt adhesive must be applied at the correct temperature. If it is too hot, it takes too long to set and if it is too cold, it can set before the materials are bonded. Hot melt glues liquefy at operating temperatures ranging from 120 to 190 degrees Celcius in the glue pot, hoses, and nozzles.
What is the heat resistance of hotmelt sealants?
The primary drawbacks of hot melts are their low heat resistance and limited strength. In contrast to other adhesives, the set-up process can be reversed, and most hot melts lose strength at 77°C. However, our selection of hot melt products can withstand extremely high temperatures—typically above 125°C.
Learn More
Sealants
Sealants are compounds formulated to create effective barriers against environmental elements, serving critical roles in diverse settings.
Sealants offer versatile solutions for applications ranging from construction to automotive and beyond. Their composition varies to address specific needs, with some sealants tailored for high-temperature environments, while others prioritize flexibility and adhesion in dynamic settings.
Sealants are integral components in construction, providing reliable bonding and sealing capabilities in structures. In automotive applications, they contribute to the assembly process, ensuring tight seals and preventing leaks. Furthermore, sealants find extensive use in manufacturing, electronics, and other industries where protection against moisture, dust, and contaminants is essential.
In addition to their fundamental sealing roles, some advanced sealants are engineered with specific properties to meet industry-specific demands. These may include resistance to harsh chemicals, extreme temperatures, or dynamic stresses. The versatility of sealants makes them indispensable in ensuring the longevity and performance of various products and structures.
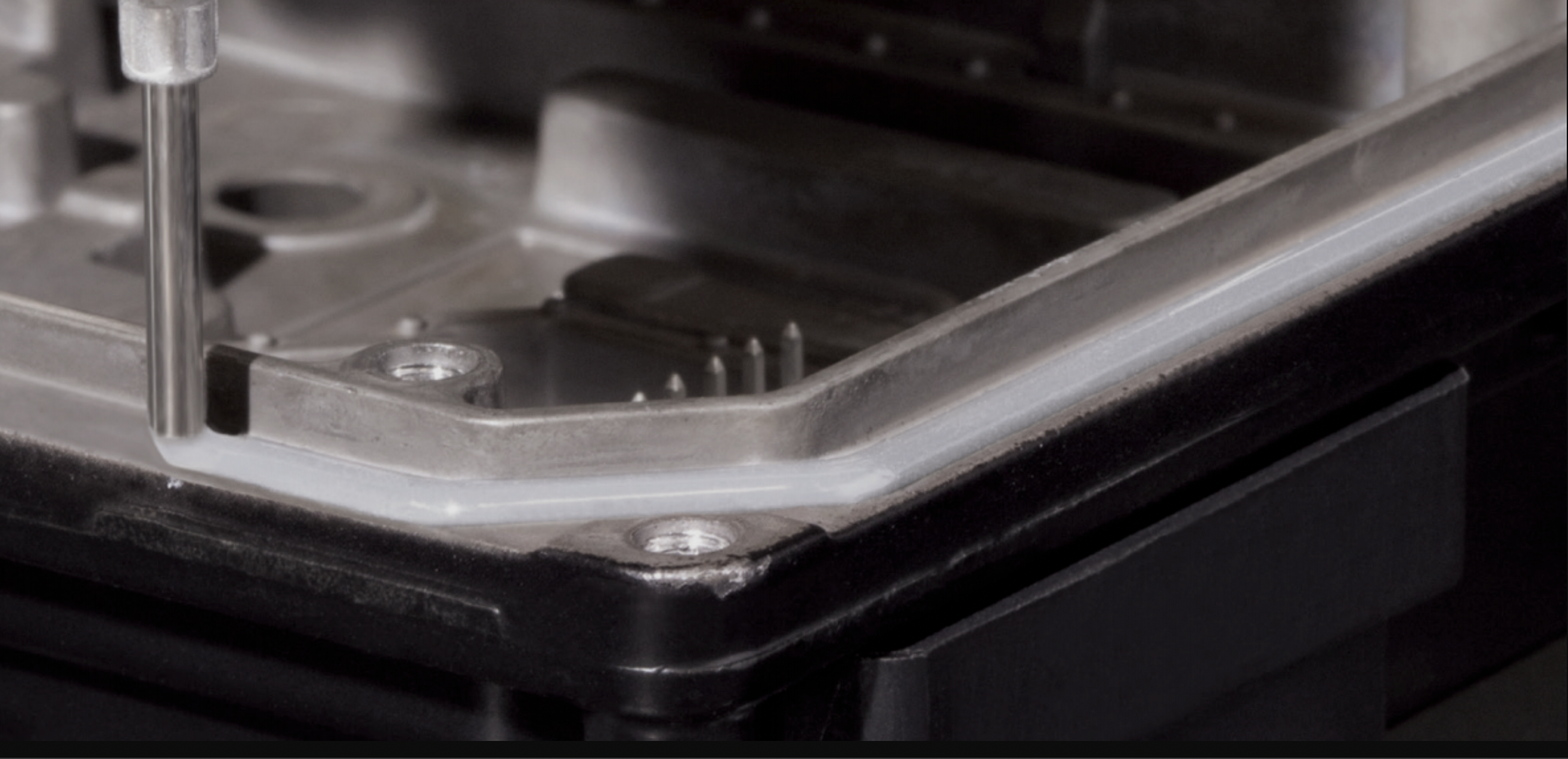

Hotmelt sealants
Hotmelt Sealants belong to the family of 1 part, solvent-free thermoplastic adhesives. These solid adhesives exhibit a low to medium viscosity (750 to 10,000 mPa.s) at dispensing temperatures, typically exceeding 195°C (383°F). They are commonly used across various industries for their ability to rapidly cool and form a robust bond after dispensing.
Common physical forms of Hotmelt Sealants include blocks, granules, candles, and sticks. Applied with melting machines, these sealants solidify upon cooling, providing reliable bonding strength. As 1 part adhesives with 100% solid thermoplastics, Hotmelt Sealants offer excellent long-term durability and resistance to moisture, chemicals, oils, and temperature extremes.
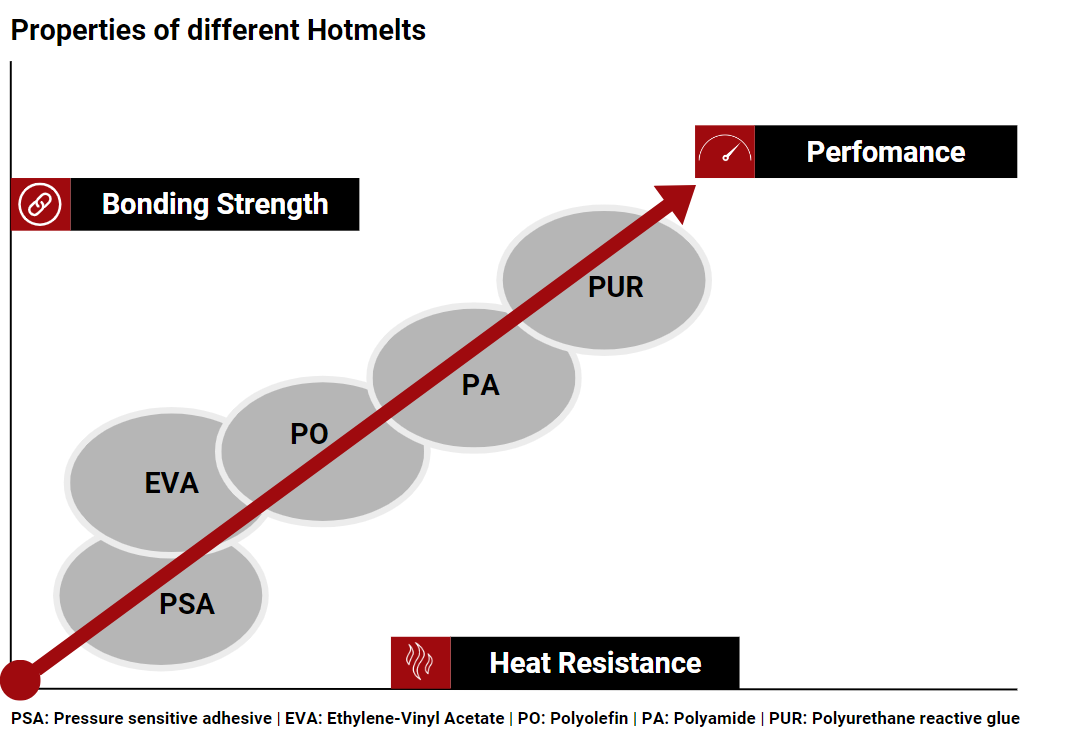
Hotmelt properties
Hotmelt Sealants showcase versatile physical properties in their cooled states, ranging from soft, rubbery, and tacky to hard and rigid. Their thermoplastic nature, coupled with 100% solid thermoplastics, makes them suitable for a wide range of applications.
Critical considerations for using Hotmelt Sealants include factors such as softening point, melt viscosity, melt index, crystallinity, tack, heat capacity, and heat stability. These factors, in addition to typical physical and adhesive strength properties, are essential for ensuring optimal performance in various scenarios.
Hotmelt Sealant types encompass pressure-sensitive adhesives (PSA), non-PSA, and reactive polyurethane hotmelt (PUR), providing diverse options to address specific application needs. Whether in packaging, automotive assembly, construction, or other industries, Hotmelt Sealants are recognized as a reliable and efficient solution for creating strong and enduring bonds.
Gaskets
Cure-in-place gaskets (CIPG)
CIPG is a sealing technology that involves applying a liquid gasket material onto a surface, which then cures or solidifies in place. This method is commonly used in industries where precise and complex shapes are required for effective sealing. The liquid gasket material typically consists of a polymer base and curing agents.
Key characteristics of CIPG include its ability to conform to irregular surfaces, creating a customized and seamless seal. This technology is known for its resistance to a wide range of temperatures, chemicals, and environmental conditions. The cured gasket provides reliable and durable sealing, making it suitable for applications in automotive engines, gearboxes, and other critical components.
CIPG properties
Polyurethane
Polyurethanes emerge as common choices for cure-in-place gaskets, particularly in the form of two-part sealants. When mixed and cured, these sealants transform into thick solids or foams, exhibiting excellent elongation and adhesion. They adhere effectively to diverse substrates, including metals, plastics, and composites. With resistance to dilute acids, bases, and light oils, polyurethane sealants generally feature hardness ratings ranging from 20 (Shore 00) to 60 (Shore A).
Silicones
RTV Silicones, lacking solvents, serve as one- or two-component sealants that cure at room temperature, with heat, or through UV light exposure. With a gap-filling capability of up to 6mm, silicones adhere well to various surfaces without requiring a primer. Operating in a temperature range from –70 to 260°C for extended periods and up to 315°C for shorter durations, RTV silicones exhibit resilience and adhesion even after thermal aging. They resist common oils and coolants, displaying excellent endurance against weathering, vibration, moisture, and ozone. Certain cure-in-place silicone sealant gaskets possess a dual-cure capability. A rapid UV cure establishes the bead, providing ample strength for assembly, followed by a moisture cure that continues, even in shaded areas, ensuring optimal strength and durability. This dual-cure feature enables the sealant to cure effectively in depths up to 6mm. However, RTV silicones have limitations, notably their relatively poor resistance to fuel and aromatic solvents. Additionally, they may not be the best choice for heavily stressed or high-pressure applications due to their lower tensile and shear strength.
Form-in-place gaskets (FIPG)
Form-in-place Gaskets (FIPG) are used for their remarkable flexibility and adaptability, seamlessly conforming to the unique shapes and contours of mating surfaces. This characteristic not only ensures precision during application but also minimizes the risk of misalignment, contributing to a consistently reliable seal.
FIPG properties
FIPG offers versatility through a range of material options, allowing customization based on specific application requirements. Commonly utilized materials such as silicone, rubber, and other elastomers provide distinct properties tailored to diverse sealing needs.The curing mechanism of FIPG is noteworthy as it typically takes place in situ, forming a durable and reliable seal as the assembly is completed. The specific curing process may involve moisture curing, heat curing, or a combination of both, depending on the formulation employed.
Form-in-Place Gaskets involve the direct application of a gasket material onto a component, creating a seal as it cures. FIPG is often preferred for its ability to automate the gasket application process, reducing labor costs and ensuring consistent results.
Similar to CIPG, FIPG materials are typically liquid or semi-liquid at the time of application and solidify to form a resilient gasket. These gaskets offer excellent adhesion to various surfaces and are widely used in industries such as electronics, appliances, and machinery.
FIPG applications
Form-in-place Gaskets (FIPG) find widespread applications across industries where precise and customized sealing solutions are indispensable. Their exceptional flexibility and adaptability make them particularly well-suited for intricate assemblies, such as those found in automotive engines, electronic enclosures, and industrial machinery. The choice of FIPG material is determined by factors such as temperature requirements, chemical compatibility, and the specific conditions of the application, ensuring optimal performance in diverse sealing scenarios.
Gasket applications
CIPG and FIPG are used in a variety of different applications, including automotive, and Electrical components.

CIPG and FIPG are extensively used in the automotive industry for sealing engine components, oil pans, transmission housings, and other critical assemblies. Their ability to withstand temperature variations and resist automotive fluids makes them indispensable in this sector.

In electronic manufacturing, CIPG and FIPG find applications in sealing and insulating electronic components. These gaskets protect against moisture, dust, and environmental contaminants, ensuring the reliability of electronic devices.