Small Outline Diodes (SOD)
Small Outline Diodes
Small outline diodes (SODs) refer to a group of semiconductor packages that are surface-mounted diodes. SODs are smaller, more compact than regular diodes, and they are designed in such a way that they can be automatically assembled onto surface mounted boards.
There are multiple variations of small outline diodes, including SOD-123, SOD-523, and SOD-923. The numbers and letters in the name typically refer to the package’s physical attributes, including their size. SOD-123 is the largest diode in the family while SOD-923 is the smallest. Some packages will also have “F” or “FL” in their names, indicating a flat lead.
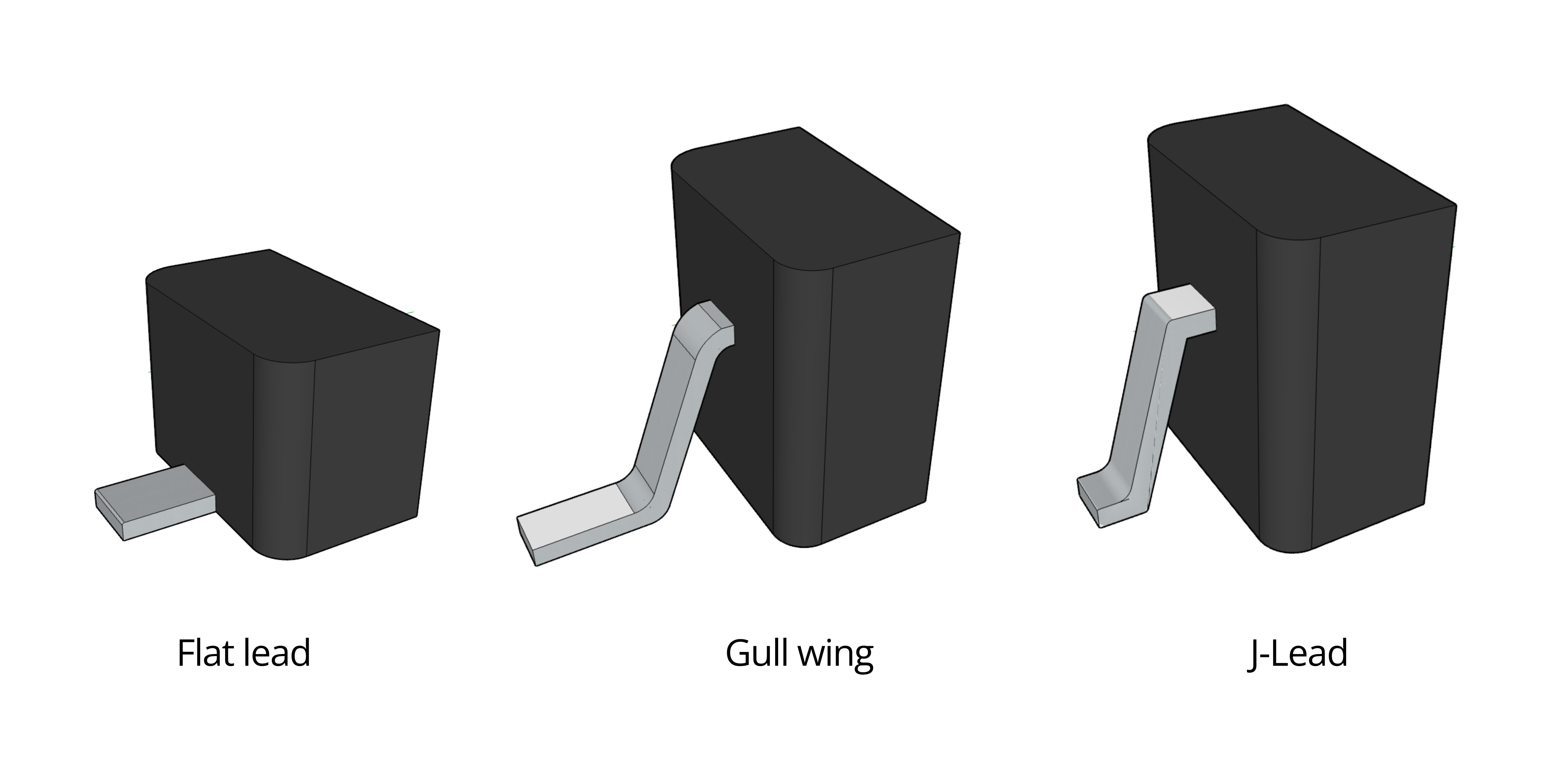
There are three general types of SODs based on their leads: gull wing, flat lead, and J lead:
Flat Lead: a metal lead that extends straight out from the side of the SOD package and parallel to the PCB when mounted. Flat lead SODs are typically used for applications requiring a straight connection.
Gull wing: this type of lead bends down then spreads away from the SOD package, resembling bird wings, hence the name “gull.” Its shape allows for solid footing to the PCB during assembly. SODs with this type of lead are more fragile and less space efficient compared to those using a J-lead. Gull-wing SODs are also cheaper but easier to work with should hand soldering be needed.
J-Lead: a metal that bends down to the bottom of the SOD package, forming a letter “J.” J-lead SODs are used for applications requiring board space efficiency, lower profile, and resistance against mechanical stresses.
Small outline diodes function like any regular rectifier diode: when positive voltage that meets the minimum threshold requirement (around 0.7V for silicon diodes) is applied to the p-side (anode), the potential barrier decreases, allowing current to flow through. On the other hand, when negative voltage is applied to the p-side, the potential barrier increases and diodes block the flow of current. Some packages have Schottky Diodes packaged in SOD-123, SOD-323, and SOD-523 variants.
SOD’s special feature is that it is small and compact, that it reduces package volume of SMT packages, and that it can be automatically assembled onto the board.
Applications of SODs
Small outline diodes can be used in surface mount technology packages that are
- Consumer electronics
- Renewable energy
- Wearable devices
Consumer Electronics
SOD packages serve a wide variety of functions in consumer electronics assembly:
| Function | Description |
| Rectification | SODs are commonly found in smartphone adapters, TVs, and audio systems. They convert AC to DC for power supplies. |
| Signal Demodulation | SODs also extract audio or data from modulated signals in receivers. |
| Voltage Regulation & Device Protection | SOD packages stabilize voltage in circuits, as an added layer of protection for voltage-sensitive components. Transient Voltage Suppression (TSV) diodes in SOD packages also provide device protection against electrostatic charges. TSV diodes are usually found in connectors and ports. |
| Switching | Fast-switching SODs handle high speed signals in microcontrollers and logic boards on mobile devices. |
| Power Management | Schottky diodes in SOD packages reduce power loss due to their low forward voltage drop, making battery usage more efficient in mobile devices. |
Renewable EnergySOD packages also provide switching, rectifying, device protection, and power management capabilities in applications related to renewable energy. However, an added application of this diode package is that they are also found in DC-DC inverters in solar & wind power systems, and that they manage power flow in Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT) controller circuits. MPPT controllers connect solar panels to DC-DC converters. When a panel experiences voltage drops, diodes (typically Schottky) packed in SOD package block reverse current from flowing back into the panels, preventing energy loss. SOD Schottky diodes also ensure that there is minimal power loss because of its lower forward voltage versus Si diodes. | Wearable DevicesLikewise, SOD’s functions in wearable devices and consumer electronics are highly similar; however, an added application under this classification of devices is that SODs are used as photodiode arrays for heart rate monitoring and optical sensors. Photodiodes convert light to electrical current. Light is shone through the skin, and the light absorbed and reflected by the skin fluctuates due to blood flowing. These fluctuations are detected by photodiodes which are then translated to electrical current that are then processed then displayed on wearable devices’ screen. SOD-123 and SOD-323 are typically the packages used in this application. |
Design Challenges in Small Outline Diodes
Because of its compact size, one of the key considerations when designing and selecting the right material for small outline diodes is thermo-mechanical stress from the die bonding process as well as the molding process brought by coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) mismatch between the die and the components of the package.
A buildup of thermomechanical stress can yield to die cracking. This is a common problem in the electronics industry and if left unaddressed, it affects the performance and reliability of electronic devices.
 (Adapted from Shi et. Al., 2012)
(Adapted from Shi et. Al., 2012) Low stress & low warpage to better manage thermo-mechanical stress buildup
Superior adhesion onto the lead frame and the die surface to prevent delamination and potential moisture contamination
High spiral flow & low viscosity both of which will ensure that the mold cavity for smaller packages such as SODs are filled and void-free.
Low ionic content to prevent corrosion and current leakage in the diode.
Excellent electrical insulation
Epoxy Molding Compounds for Surface Mount Small Outline Diodes
| Products | Key features |
| Hysol KL 6500S | Low stress; High reliability |
| Hysol GR 646 | Ultra fast cure material |
| Hysol GR 640HV-L1 | Up to MSL1;Good electrical performance;Cleaning cycle more than 1000 continuous shots; Suitable for eutectic bonding process |
| Hysol GR 640HV-LV | Good wire sweep performance |
| Hysol GR 640HV-FF | Fine filler cut; MSL1 performance; Suitable for ultra-small outline device such as SOD923 |
| Hysol GR 640HV-L1(M7A) | Up to MSL1; Super electrical performance; Cleaning cycle more than 1000 continuous shots; Suitable for eutectic bonding process |
| Hysol GR 510-HP | Pass MSL3 for big body size such as SOT223/SOT89 |
| Hysol GR 720 | For die attach paste bonded SOT;Low stress; Good workability; Good delam & electrical performance |
All products are Green
Frequently Asked Questions About Small Outline Diodes
What’s the difference between Small Outline Transistors (SOT) and SODs?
From the name itself, the difference is in the fuction: SOTs are transistors, while SODs are small diodes. Transistors are controlled switches while diodes are uncontrolled switches. SODs usually have rectifier, Schottky, or TVS diodes as the device in the package while SOTs have BJTs, MOSFETs, LDOs, or logic ICs within the package. SODs are also smaller in size and typically only have 2 pins (SOTs have 3 to 6).


