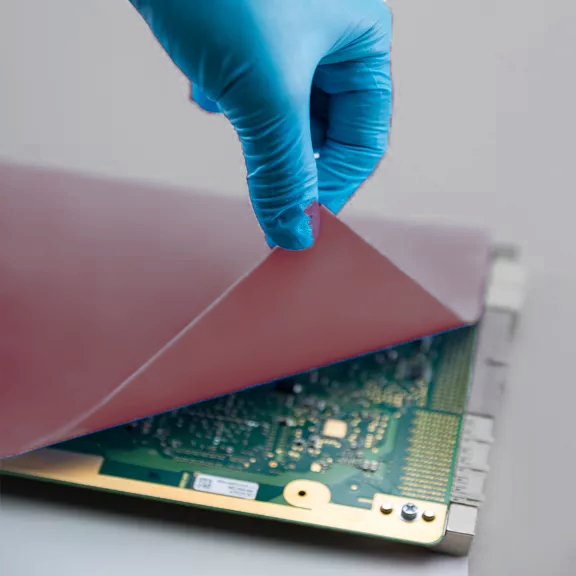
TGP 7500C | Thermal Gap Pad
- 0.16 Thermal Impedance
- 7.5 Thermal Conductivity
- Excellent surface wetting
Product Description
TGP7500C Thermal Conductive Gap Pad delivers exceptional thermal performance with minimal assembly stress, making it ideal for high-power electronic applications such as power modules, automotive ECUs, telecom hardware, and high-density CPUs/GPUs. Its ultra-high compressibility ensures optimal interface contact—even with uneven or delicate surfaces—reducing air gaps and enhancing thermal transfer.
Product Key Features:
- High thermal performance (7.5W/m•K thermal conductivity & 0.16 °C•cm²/W thermal impedance) — designed to minimize thermal resistance
- Ultra-high compressibility for low stress applications
- Available in different thickness (0.5-5.0mm with 0.25mm incremental)
TGP7500C is engineered to minimize thermal resistance across the interface by leveraging its soft silicone matrix filled with high-performance ceramic particles. It maintains stable performance across thermal cycling and humidity testing, ensuring long-term reliability in mission-critical environments.
Thickness range:
- 0.5-5.0mm with 0.25mm incremental
Thickness Tolerance: >1mm, ±10%
- 0.5-1mm, ±0.1mm
- <0.5mm, ±0.05mm
Applications
- Thermal management in different electronic applications such as in power conversion equipment, semiconductor memory modules, and high performance servers.
Technical Specifications
| General Properties | |
| Color Color The color | Brick Red |
| Specific Gravity Specific Gravity Specific gravity (SG) is the ratio of the density of a substance to the density of a reference substance; equivalently, it is the ratio of the mass of a substance to the mass of a reference substance for the same given volume. For liquids, the reference substance is almost always water (1), while for gases, it is air (1.18) at room temperature. Specific gravity is unitless. | 3.5 |
| Thermal Properties | |
| Operating Temperature | -40 - 150 °C |
| Thermal Conductivity Thermal Conductivity Thermal conductivity describes the ability of a material to conduct heat. It is required by power packages in order to dissipate heat and maintain stable electrical performance. Thermal conductivity units are [W/(m K)] in the SI system and [Btu/(hr ft °F)] in the Imperial system. | 7.5 W/m.K |
| Thermal Impedance | 0.16 °C·cm²/W |
| UL 94 Rating UL 94 Rating Flammability rating classification. It determines how fast a material burns or extinguishes once it is ignited. HB: slow burning on a horizontal specimen; burning rate less than 76 mm/min for thickness less than 3 mm or burning stops before 100 mm V-2: burning stops within 30 seconds on a vertical specimen; drips of flaming particles are allowed. V-1: burning stops within 30 seconds on a vertical specimen; drips of particles allowed as long as they are not inflamed. V-0: burning stops within 10 seconds on a vertical specimen; drips of particles allowed as long as they are not inflamed. 5VB: burning stops within 60 seconds on a vertical specimen; no drips allowed; plaque specimens may develop a hole. 5VA: burning stops within 60 seconds on a vertical specimen; no drips allowed; plaque specimens may not develop a hole | V-0 |
| Electrical Properties | |
| Dielectric Strength Dielectric Strength Dielectric strength is measured in kV per mm and is calculated by the Breakdown voltage divided by the thickness of the tested material. Those two properties go hand in hand and while Breakdown voltage is always thickness dependent, dielectric strength is a general material property. As an example, the dielectric strength of Polyimide is 236 kV/mm. If we place 1mm of Polyimide between two electrodes, it will act as an insulator until the voltage between the electrodes reaches 236 kV. At this point it will start acting as a good conductor, causing sparks, potential punctures and current flow. | 7 kV/mm |
| Volume Resistivity Volume Resistivity Volume resistivity, also called volume resistance, bulk resistance or bulk resistivity is a thickness dependent measurement of the resistivity of a material perpendicular to the plane of the surface. | 1.0x1015 Ohms⋅cm |